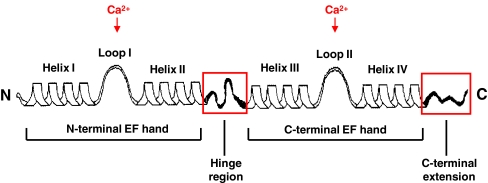
Fig. 1.
Schematic depiction of the secondary structure of an S100 protein. Each S100 monomer consists of a repetitive Ca2+ binding EF-hand motif whereas the N-terminal (non-canonical) and C-terminal (canonical) EF hand are connected by a linker region (hinge region). The hinge region and C-terminal extension (boxed in red) display the greatest sequence variability among individual members of the S100 protein family. Reproduced with modifications from Donato et al. [11]