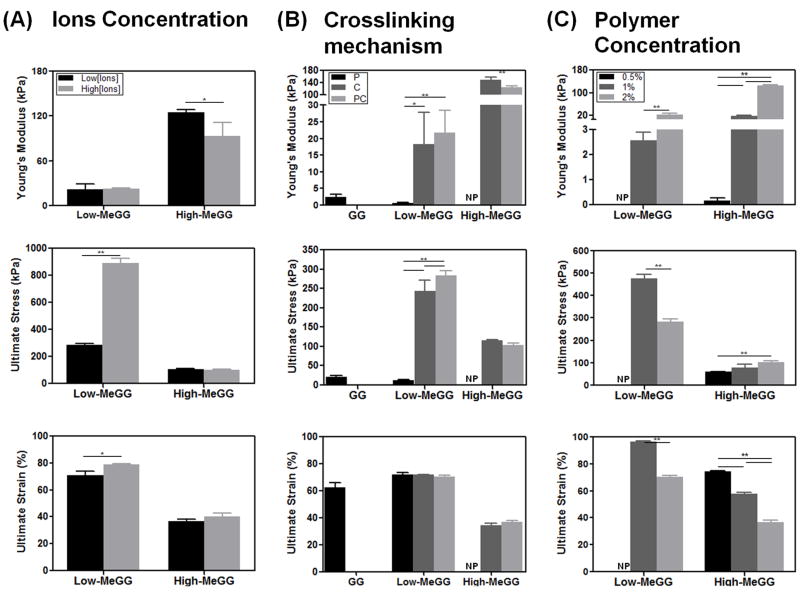
Fig. 5.
Mechanical properties of GG and MeGG hydrogels: Young’s Modulus, Ultimate stress and Ultimate strain. The influence of three parameters over the mechanical properties of the hydrogels was evaluated: (A) Concentration of ions in the hydrogel fabrication; (B) Type of crosslinking mechanism (P, C or PC); and (C) Polymer concentration. The mechanical properties of the developed hydrogels showed to be highly dependent on the ionic content, type of crosslinking, methacrylation degree and polymer concentration. Statistical analysis through two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-hoc test showed significant differences (***p<0.0001, **p<0.001, *p<0.01) between the analyzed groups. NP: not processable.