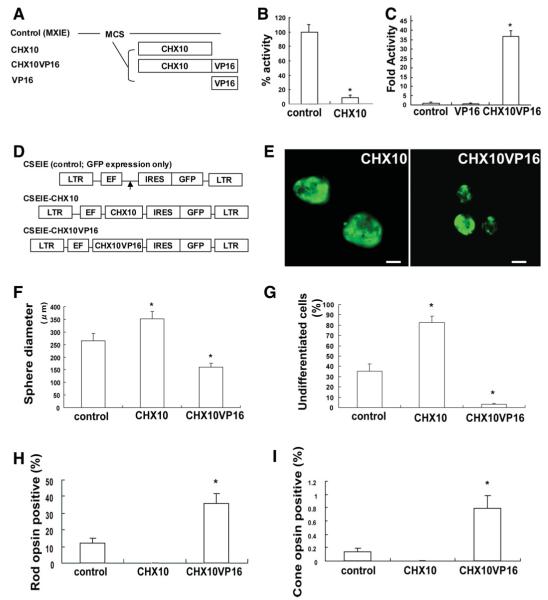
Figure 1.
Modulation of CHX10 expression is important for induction and early maturation of photoreceptors from human retinal stem cell (hRSC) progeny. (A): Schematic illustration of effecter vectors encoding CHX10, CHX10VP16 or VP16. CHX10VP16 encodes human CHX10 fused to amino acids 410-490 of the VP16 activation domain. All genes were introduced into the pMXIE expression vector. (B): The expression vector pMXIE-CHX10 represses activation. NG108 cells were cotransfected with equimolar amounts of control effector plasmid or pMXIE-CHX10 along with GAL4-HSF1 activator and HD4-pG5EC chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) reporter containing four homeodomain binding sites and five GAL4 DNA binding sites. One hundred percent CAT activity is taken as that obtained in the presence of control effector plasmid was set to 1.0. The y-axis indicates the percentage of reporter transcription with CHX10 transfection/reporter transcription with control transfection. *p < .05 indicates statistically significance with Student’s t test. (C): Transcription is activated by pMXIE-CHX10VP16. NG108 cells were cotransfected with equimolar amounts of control effector plasmid or pMXIE-CHX10VP16 along with HD4-pG5EC CAT reporter. The y-axis indicates fold activity of reporter transcription with VP16 or CHX10VP16 transfection/reporter transcription with control transfection set to 1.0. *p < .05 indicates statistically significance with analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Dunnette’s multiple comparison test. (D): Schematic of replication-defective self-inactivating lentiviral vectors containing an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) sequence followed by enhanced green fluorescent protein (GFP) (CSEIE). CHX10 or CHX10VP16 cDNA were cloned into CSEIE, which directs the expression of the cloned genes together with GFP from the internal promoter, EF1α. Control vector expresses only GFP. (E): Human retinal stem cells-derived sphere transfected with CHX10 (left) and CHX10VP16 (right). Spheres ubiquitously express GFP, but some of the cells in the clonal sphere are pigmented, thus obscuring GFP and producing a mottled GFP appearance in the spheres. Scale bar: 100 μm. (F): Sphere diameters that are a proxy for total cell number generated by proliferation were measured in control, CHX10, or CHX10VP16-induced retinal stem cell (RSCs) colonies. We measured more than 30 spheres in each group in at least three independent experiments. Sphere diameters were significantly increased in CHX10-induced clonally-derived RSC colonies compared with control. On the other hand, sphere diameters were significantly decreased in CHX10VP16-induced clonally-derived RSC colonies (analysis of variance and Dunnette’s multiple comparison test, *p < .05). (G): PAX6/NESTIN double labeling cells, which indicate undifferentiated retinal cells, were measured in the in vitro differentiation assay with hRSC colonies transfected with control, CHX10,or CHX10VP16. With CHX10 transduction, most of hRSC progeny maintained an undifferentiated state. In contrast, CHX10VP16 transduction significantly decreased the number of undifferentiated cells (ANOVA and Dunnette’s multiple comparison test, *p < .05). The y-axis indicates the percentage of PAX6/NESTIN double labeling cells /total cell number after neomycin selection. (H,I): CHX10 transduction abolished photoreceptor cell differentiation, while CHX10VP16 transduction significantly increased rod (H) and cone (I) photoreceptor differentiation. Rho1D4 was used as a rod photoreceptor marker and human cone arrestin as a cone photoreceptor marker. CHX10 transduction abolished photoreceptor cell differentiation, whereas CHX10VP16 transduction significantly increased rod and cone photoreceptor differentiation (Student’s t test, *p < .05). The y-axis indicates the percentage of photoreceptor marker and GFP coexpressing cell number/GFP expressing cell number. Abbreviations: EF, elongation factor; GFP, green fluorescent protein; IRES, internal ribosome entry; LTR, long terminal repeat.