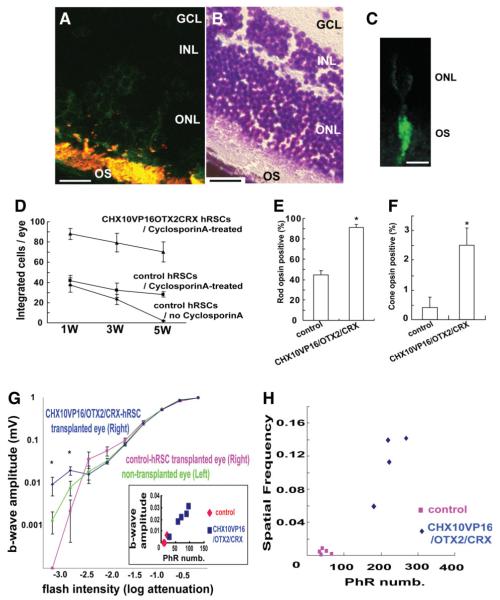
Figure 4.
In vivo human retinal stem cell (hRSC) transplantation into mouse eye. (A): Human retinal stem cell progeny (green fluorescent protein [GFP] positive) are immunostained with a photoreceptor marker Rom1 (red), which marks a outer segment protein in transplanted human (double labeled with two markers shown as yellow) and host (red) CD1 retinal cells (scale bar: 100 μm). GCL; retinal ganglion layer, INL; inner nuclear layer, ONL; outer nuclear layer, OS; outer segment. (B): Mouse retina section (adjacent to the one shown in A) stained with cresyl violette to show the retinal location of the transplanted human cells shown in (A) (scale bar: 100 μm). (C): High-power image of a single hRSC-derived phtotoreceptor (GFP positive) integrated into the host retina. The human donor cell shows the morphology of a photoreceptor (scale bar: 20 μm). (D): Transplanted hRSC progeny transfected with CHX10VP16/OTX2/CRX show improved integration and survival compared with control transfection at 1, 3, and 5 weeks after transplantation. (E,F): Improved photoreceptor differentiation in hRSC progeny transfected with CHX10VP16/OTX2/CRX compared with control transfected cells at 5 weeks after transplantation (rods (E) and cones (F)) (analysis of variance [ANOVA] and Dunnette’s multiple comparison test, *p < .05). Rho1D4 was used as a rod photoreceptor marker and human cone arrestin as a cone photoreceptor marker. The y-axis indicates the percentage of photoreceptor marker and GFP coexpressing cell number/GFP expressing cell number. (G): At the lowest flash intensities (−3.2 and −2.8) the CHX10VP16/OTX2/CRX group shows a higher response than the nontransplanted and GFP-only vector-treated groups (ANOVA and a Dunnette’s multiple comparison test, *p < .05). Inset shows that a significant correlation of maximal b wave response and surviving human photoreceptor cell number (PhR numb) was seen. For reasons of space within this inset, the two data points for the control animals represent the data from four animals. (H): As a within-animal control in the transplantation model, the differences in the minimal spatial frequency detected between the transplanted eye (right) and nontransplanted eye (left) in each individual mice were estimated. Abbreviations: GCL, retinal ganglion layer; hRSCs, human retinal stem cells; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OS, outer segment.