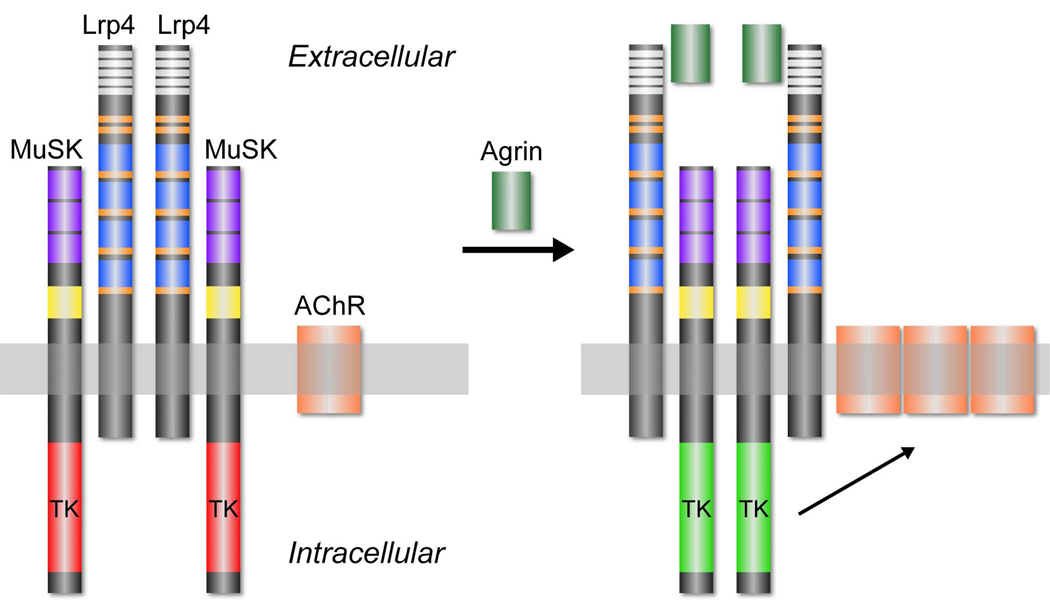
Figure 6.
Cartoon illustrating interactions between neural Agrin, Lrp4 and MuSK. Lrp4 self-associates and interacts with MuSK in the absence of Agrin (left). The arrangement of Lrp4 and MuSK within this complex is not known, and the complex may be oligomeric rather than dimeric, as depicted. Moreover, the domains responsible for the Lrp4-Agrin and Lrp4-MuSK interactions are not known. Neural Agrin binds to the preformed complex and triggers a reorganization or reorientation of MuSK, promoting trans-phosphorylation and kinase activation (right). Once phosphorylated, MuSK activates a signaling pathway that leads to synaptic differentiation, including clustering of AChRs. Domain coloring for Lrp4: white, LDLa; orange, EGF-like; blue, b-propeller. Domain coloring for MuSK: purple, immunoglobulin-like; yellow, Frizzled-like cysteine-rich; red or green, tyrosine kinase (TK).