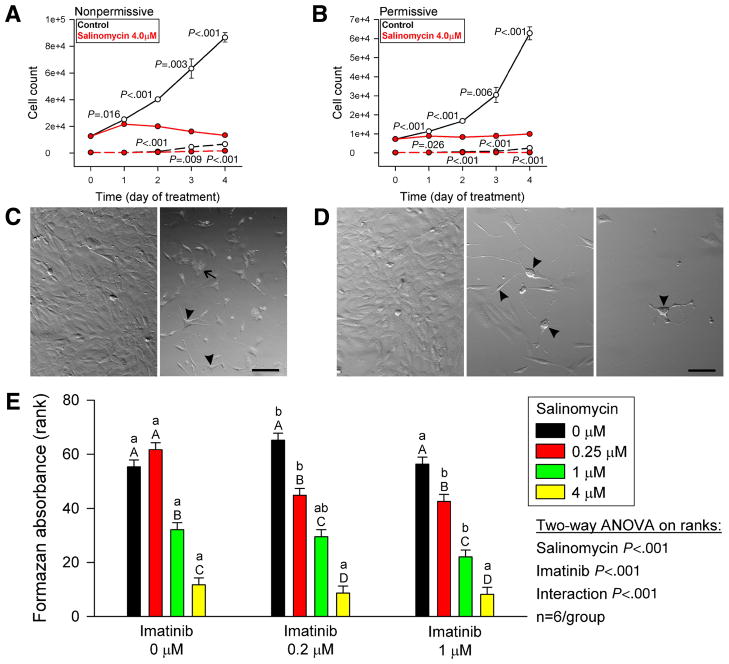
Figure 7. Salinomycin inhibits the proliferation of ICC stem cells and sensitizes them to imatinib.
(A,B) Effects of salinomycin on the proliferation of D2211B cells. Solid lines, PI− cells; dashed lines, PI+ (dead) cells. Note nearly complete inhibition. The number of PI+ dead cells was also reduced. (C) Morphology of D2211B cells cultured under nonpermissive conditions with vehicle (left panel) or salinomycin (right panel) for 4 days. Arrowhead, multipolar, ICC-like cells. Arrow, fibroblast-like cell filled with cytoplasmic vesicles. Scale bar, 25 μm. (D) Morphology of D2211B cells cultured under permissive conditions with vehicle (left panel) or salinomycin (middle and right panels) for 4 days. Note ICC-like phenotype of salinomycin-treated cells (arrowheads). Scale bar, 25 μm. (E) Dose-dependent effects of 5-day combined treatments with salinomycin and imatinib on the proliferation of D2211B cells under permissive conditions. The rank of 1 was assigned to the culture with the lowest cell number. Groups not sharing the same labels were different by post-hoc multiple comparisons. Lowercase and uppercase labels apply to groups receiving the same salinomycin and imatinib doses, respectively.