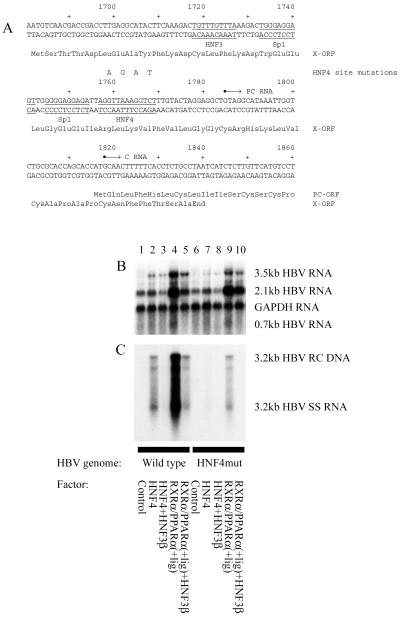
Figure 3.
The proximal nucleocapsid HNF4 binding site is a major determinant of nuclear hormone receptor-mediated HBV replication in mouse fibroblasts. (A) Sequence of the HBV core promoter region. The 4-nt HNF4 site mutation indicated above the wild-type sequence inhibits the binding of nuclear hormone receptors to the proximal HNF4 binding site (results not shown). The nucleotide substitutions do not alter the X-gene polypeptide sequence. The HNF3 and Sp1 binding sites are also indicated. (B and C) Mouse NIH 3T3 fibroblasts were transiently transfected with HBV DNA (4.1 kbp) constructs and liver-enriched transcription factors. The HBV HNF4mut DNA (4.1 kbp) construct (lanes 6–10) contained the 4-nt mutation (A) in the proximal HNF4 binding site of the core promoter. Both core promoter regions in this terminally redundant HBV construct (Fig. 1A) were mutated for this analysis, but similar results were obtained when only the upstream core promoter region was mutated (results not shown). (B) RNA (Northern) filter hybridization analysis of HBV transcripts. (C) DNA (Southern) filter hybridization analysis of HBV replication intermediates.