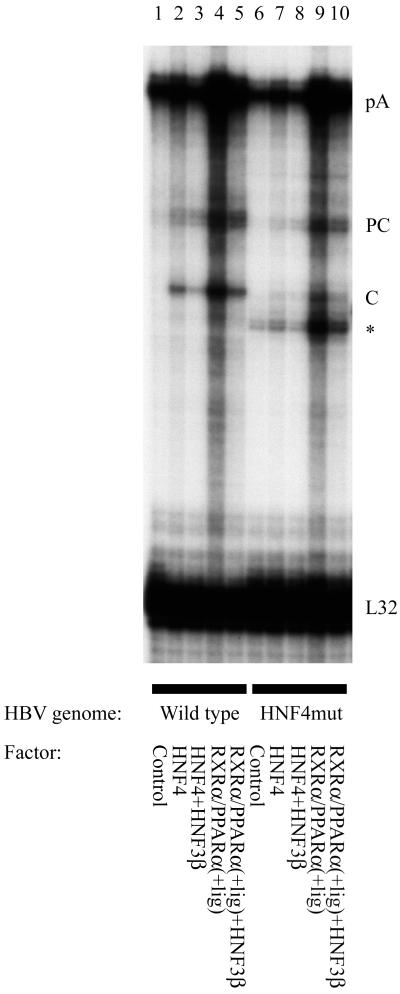
Figure 4.
Effect of HNF3 and mutation of the proximal nuclear hormone binding site in the core promoter on the transcription initiation site of the 3.5-kb HBV RNA. Mouse NIH 3T3 fibroblasts were transiently transfected with HBV DNA (4.1 kbp) constructs and liver-enriched transcription factors. The HBV HNF4mut DNA (4.1 kbp) construct (lanes 6–10) contained the 4-nt mutation (Fig. 3A) in the proximal HNF4 binding site of the core promoter. Both core promoter regions in this terminally redundant HBV construct (Fig. 1A) were mutated for this analysis. RNase protection analysis was performed to map the transcription initiation sites of the HBV precore (PC) and pregenomic or core (C) transcripts. The HBV probe also protected a fragment (pA) derived from the 3′ end of all of the HBV RNAs that terminated at the HBV polyadenylation site. The protected fragment indicated with an asterisk is generated as a result of the cleavage of the pA-protected fragment at the site of the discontinuity between the wild-type probe and the HNF4mut containing HBV RNA. A riboprobe detecting the ribosomal gene L32 transcripts was included as an internal control.