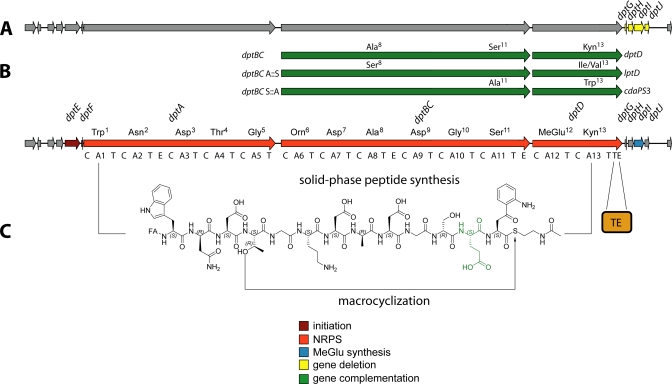
FIGURE 3.
Overview of the methods utilized for the generation of daptomycin derivatives employing the native gene cluster. Structural diversity can be generated in vivo, as depicted by gene deletion (A) and trans-complementation (B) approaches. For trans-complementation, dptBC and dptD were substituted with homologous genes, leading to amino acid substitutions. Combinations of this set of genes with deletions and module exchanges afforded numerous daptomycin analogs. C, in vitro chemoenzymatic synthesis of daptomycin derivatives employing linear activated peptidyl thioesters that substitute the assembly line and the recombinant TE domain. The modified MeGlu12 residue is shown in green.