FIGURE 1.
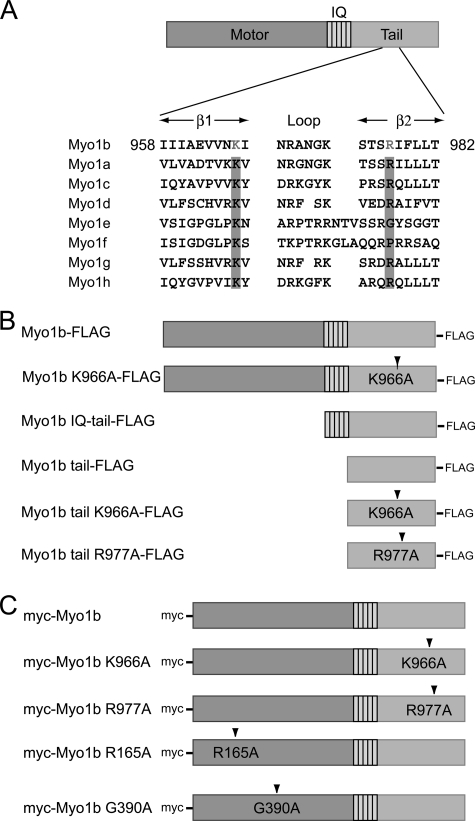
Schematic diagram of rat Myo1b and constructs used in this study. A, rat Myo1b structure and alignment of the β1-loop-β2 motif of the PH domain of class I myosins. The rat Myo1b isoform used in this study consists of a motor domain, a neck domain with five IQ domains, and a tail domain. The tail domain of Myo1b contains the β1-loop-β2 motif of a putative PH domain in which conserved basic residues are highlighted. Conserved basic residues in other class I myosins are also highlighted. The GenBankTM accession numbers of the myosin isoforms are as follows: Myo1b, CAA48287; Myo1a, EDM16453; Myo1c, CAA52807; Myo1d, CAA50871; Myo1e, CAA52815; Myo1f, NP_001101546; Myo1g, NP_001128315; and Myo1h, NP_001158045. B, Myo1b constructs used in in vitro experiments. A FLAG tag was fused to the C terminus of full-length Myo1b, Myo1b IQ-tail (Asp706–Pro1107), or the Myo1b tail fragment only (Val824–Pro1107). Lys966, a conserved basic residue in the β1-loop-β2 motif, was replaced with alanine in full-length Myo1b K966A-FLAG and Myo1b tail K966A-FLAG. Also, Arg977 was replaced with alanine in Myo1b tail R977A-FLAG. C, constructs used for expression in mammalian cells. A Myc tag was fused at the N terminus to full-length wild-type Myo1b, the full-length Myo1b tail K966A mutant, or the full-length Myo1b tail R977A mutant. Mutations R165A and G390A reside in switches I and II, respectively, critical regions of the myosin motor domain.