FIGURE 4.
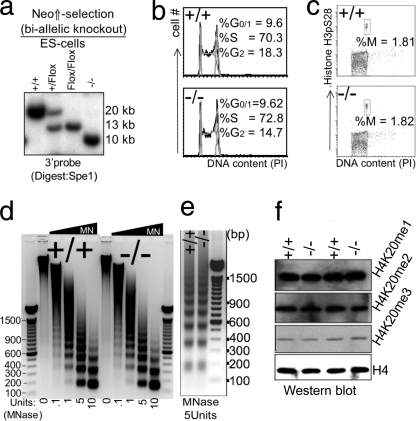
Impact of disruption of L3mbtl1 on ES cells. a, biallelic disruption of L3mbtl1 in ES cells was achieved after selection of clones that had duplicated the targeted allele by crossing over in the presence of increased neomycin concentration (third lane). After confirmation of a normal karyotype (not shown), both alleles of L3mbtl1 were disrupted by transient expression of Cre (right lane). b, no major differences in cell cycle profiles (G1, S, and G2/M) of L3mbtl1−/− ES cells compared with control ES cells. Analysis of cell cycle distribution after staining DNA content with propidium iodide (PI) is shown. c, the G2/M checkpoint is not altered in L3mbtl1−/− ES cells. Simultaneous staining for DNA content and serine 28-phosporylated histone H3 (H3pS28) was used to resolve G2 and M phases of the cell cycle. d and e, analysis of global chromatin structure using limited micrococcal nuclease (MNase) digests of wild type or L3mbtl1−/− ES cells. Micrococcal nuclease cuts DNA that is not occupied by nucleosomes. In dense chromatin or with limited amounts of enzyme, digestion within the internucleosomal spaces is inefficient, resulting in the generation of oligo- and multinucleosomes with distinct sizes (the lowest band represents mononucleosome; higher bands represent oligonucleosome (dimers, trimers, etc.)). In loose (relaxed) chromatin and with high amounts of micrococcal nuclease, fragments representing DNA protected by a single nucleosome are generated preferentially. Note that an equal abundance of the various bands suggests that there is no marked global difference in compaction of chromatin after disruption (e); an equal size of fragments demonstrates that nucleosome spacing is not affected by loss of L3MBTL1. Each panel shows one representative of three independent experiments. DNA markers are shown with sizes of prominent bands labeled. f, global levels of H4K20 mono-, di-, or trimethylation are not affected by the absence of L3MBTL1 in ES cells.