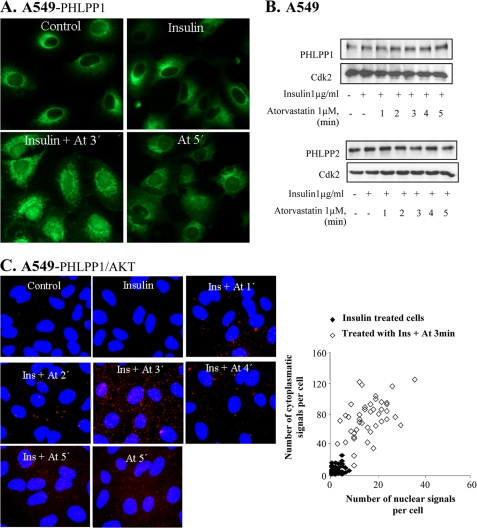
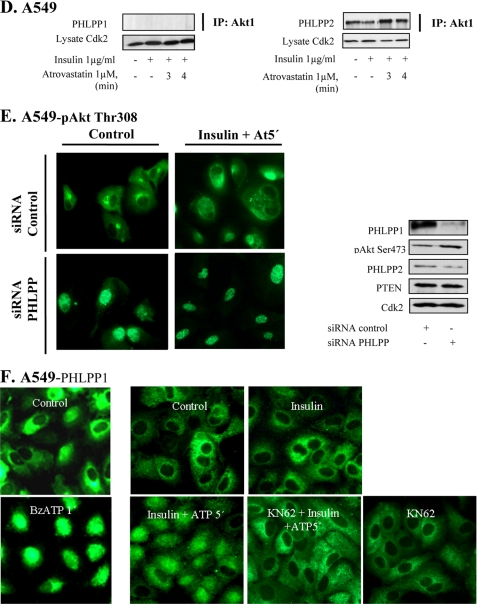
FIGURE 1.
Atorvastatin and BzATP induce nuclear localization of PHLPP and binding to Akt. In A–D, A549 cells were treated with insulin (1 μm for 15 min) and thereafter with atorvastatin (1 μm for 1–5 min) as indicated. In E, cells were transfected with siRNA against PHLPP (50 nm) for 72 h and thereafter treated with insulin (1 μg/ml for 15 min) and atorvastatin (1 μm for 5 min). In F, cells were treated with KN-62 (100 nm for 10 min) and thereafter with BzATP or ATP (100 μm for 1–5 min) as indicated. In A and F, cells were stained for PHLPP1, and in E, they were stained for pAkt Thr308. In B, samples were then analyzed by Western blotting, employing antibodies for PHLPP1 and PHLPP2. Cdk2 was used as a loading control. In C, protein-protein interactions between Akt and PHLPP1 were studied employing PLA. Purple dots indicate proximity between cellular bound antibodies. The purple dots were counted using MATLAB, and the distribution of PHLPP1/AKT PLA signals between the nucleus and the cytoplasm is shown in insulin-treated (n = 50) or insulin plus atorvastatin-treated cells (n = 50) (each square represents a single cell). In D, lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) using an Akt1 antibody and analyzed employing antibodies for PHLPP1 or PHLPP2. Total lysates were analyzed for Cdk2 (loading control).