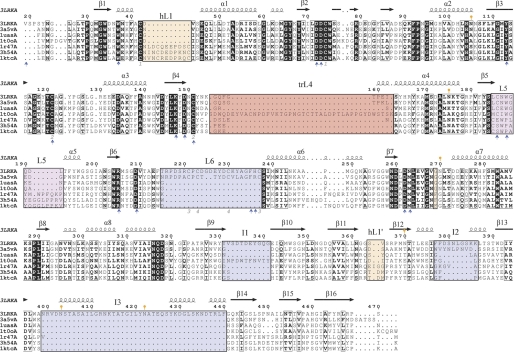
FIGURE 7.
Structural alignment of GH27 members. The structural alignment of ScAGal (3LRKA), the α-galactosidases from U. vinacea (3a5vA), rice (1uasA), T. reesei (1t0oA), H. sapiens (1r47A), and the α-N-acetyl-galactosaminidases from H. sapiens (3h54A) and G. gallus (1ktcA) was generated with the DALI server (45) and ESPript (46). ScAGal secondary structure is shown above the sequence alignment. The black squares indicate sequence similarity. The insertions in ScAGal loops (L6, I1, I2, and I3) are highlighted with a blue box. Those insertions involved in dimerization in human and chicken enzymes are highlighted with orange boxes, and the 2-position recognition loop, at L5, is in the magenta square. The insertion in T. reesei L4 is highlighted with a red box. Gray numbers refer to disulfide bonds in the ScAGal structure. Orange marks refer to glycosylated asparagines. Blue arrows highlight the residues involved in substrate recognition. B. halodurans α-galactosidase is more distant from the eukaryotic enzymes, and some motifs are unconserved. A full structural alignment containing also the prokaryotic enzyme is given in (supplemental Fig. S2).