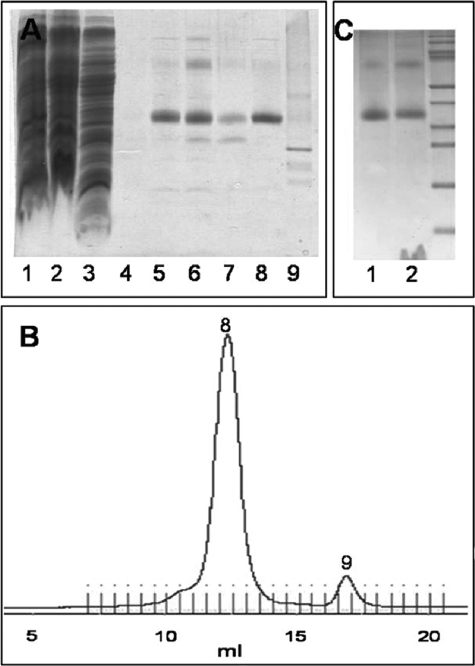
FIGURE 2.
Purification and reconstitution of spin-labeled KtrBThr-318R1-His6. A, SDS-PAGE during solubilization and purification. Lane 1, membrane fraction; lane 2, supernatant after solubilization of the membrane fraction; lane 3, flow-through of the Ni2+-NTA column after 1 h of binding the solubilisate to it; lane 4, flow-through after spin label binding to the protein on the column and extensive washing with buffer W with 50 mm imidazole without β-mercaptoethanol; lanes 5–7, elution fractions E1–E3 of the spin-labeled protein from the Ni2+-NTA column with buffer W with 500 mm imidazole without β-mercaptoethanol; lane 8, spin-labeled KtrBThr-318R1-His6 eluted at 12.5 ml via gel filtration in buffer W without imidazole and β-mercaptoethanol; lane 9, degradation product of KtrB separated via gel filtration at 17.5 ml. 10 μl of a sample were added per lane. B, chromatogram giving A280 against the volume (in ml) of the gel filtration of the spin-labeled KtrBThr-318R1-His6 variant in buffer W without β-mercaptoethanol on a Superdex 200 column. Numbers 8 and 9 correspond to the fractions analyzed in lanes 8 and 9 of A, respectively. C, SDS-PAGE of the reconstitution of spin-labeled KtrB variants. Lane 1, 5 μg of solubilized protein; lane 2, the theoretically equivalent amount of KtrB after reconstitution in liposomes from E. coli phospholipids and egg l-α-phosphatidylcholine.