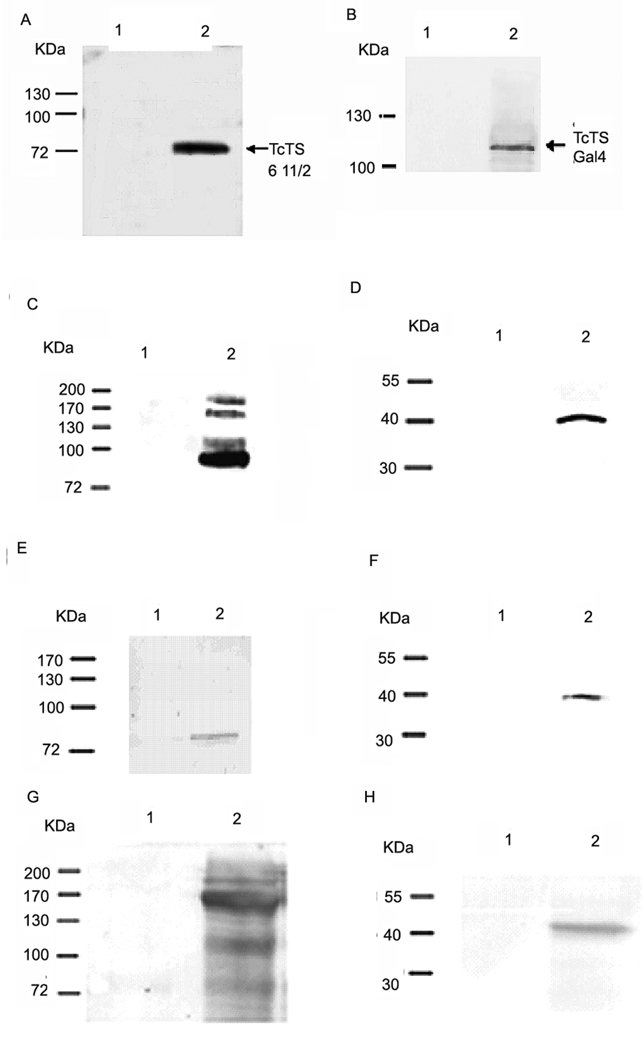
Fig. 2. Verification of a trans-sialidase antibody and Interactions of TcPKAc with the members of trans-sialidase super family.
A commercial anti- sialidases antibody (rabbit) was first tested and verified for its ability to recognize T. cruzi trans-sialidases recombinant proteins, including a purified active trans-sialidase and trans-sialidase fusion proteins in crude yeast lysates (primary antibody dilution 1:1000; secondary antibody dilution 1: 5000) (Fig.2A–B). Co-immunoprecitation was performed using Triton X-100 protein extracts from trypomastigotes and a trans-sialidase polyclonal antibody (anti-TCTS 6 11/2, mouse), a commercial sialidase antibody, a T. cruzi SA85-1.1polyclonal antibody (rabbit) and a TcPKAc mAb(antibody dilutions:1;100 for immunoprecipitation, 1:1000 for immunoblot)(Fig.2C–H).
A. The sialidase antibody binds to recombinant protein of TCTS 611/2.
Lane1, 100ug of BSA as negative control;
Lane 2, 100ng of recombinant protein of TCTS 611/2.
B. The sialidase antibody binds to fusion protein of trans-sialidase (Tc00.1047053509187.10) in yeast lysate.
Lane 1, 150 ug of wild type yeast lysate without transformation as negative control;
Lane 2, 150ug of yeast lysate with transformation of both bait and pAD- trans-sialidase (Tc00.104053509187.10) constructs. Antibody recognized the pAD- trans-sialidase protein.
C. Co-IP in Triton X −100 protein extracts from trypomastigotes with a TcPKAc mAb. Complex pulled down by a TcPKAc mAb contained proteins recognized by a commercial sialidase antibody on immunoblot.
Lane 1, Negative control using an unrelated mAb (anti-bag5);
Lane 2, Immunoprecipitation with TcPKAc mAb. There are four bands ranged from 85 kDa to 200 kDa, which reacted with this sialidase antibody.
D. Co-IP in Triton X −100 protein extracts from trypomastigotes with a commercial sialidase antibody. The sialidase antibody was able to pull down a protein, which reacted with a TcPKAc mAb on immunoblot.
Lane 1, negative control using pre-immune rabbit serum;
Lane 2, Immunoprecipitation with Trans-sialidase antibody. There is a 40-kDa TcPKAc protein band.
E. Co-IP in Triton X −100 protein extracts from trypomastigotes with a TcPKAc mAb.
Complex pulled down by a TcPKAc mAb contained proteins recognized by a SA85-1.1 antibody on immunoblot.
Lane 1, Negative control using an unrelated mAb (anti-bag5);
Lane 2, Immunoprecipitation with TcPKAc mAb. There is an 85 kDa SA85-1.1 protein band.
F. Co-IP in Triton X −100 protein extracts from trypomastigotes with a SA85-1.1 antibody.
Precipitated complex by a SA85-1.1 antibody contained TcPKAc.
Lane 1, Negative control using pre-immune rabbit serum;
Lane 2, Immunoprecipitation with SA85-1.1 antibody. There is a 40-kDa TcPKAc protein band.
G. Co-IP in Triton X −100 protein extracts from trypomastigotes with a TcPKAc mAb. Complex pulled down by a TcPKAc mAb contained proteins recognized by a trans-sialidase antibody (anti-TCTS 6 11/2) on immunoblot.
Lane 1, Negative control using an unrelated mAb (anti-bag5);
Lane 2, Immunoprecipitation with TcPKAc mAb. There are bands with molecular weights from 85–200 kDa.
H. Co-IP in Triton X −100 protein extracts from trypomastigotes with a TCTS 6 11/2 antibody. Precipitated complex by a TCTS 6 11/2 antibody contained TcPKAc.
Lane 1, Negative control using pre-immune mouse serum;
Lane 2, Immunoprecipitation with Anti-TCTS 6 11/2;