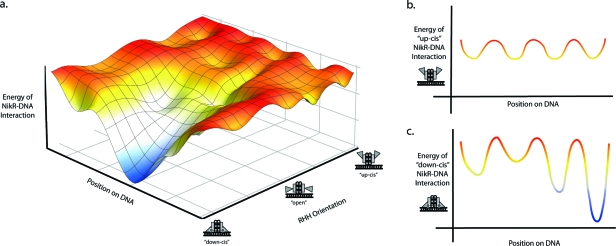
Figure 6.
Hypothetical energy landscape for NikR when bound to DNA. In panel (a), both the orientation of the RHH domains and the position on DNA are considered. When the RHH domains are in the down-cis position and NikR is at the correct DNA binding sequence, there is an energy minimum (blue well). As the RHH domains assume a more “out” position, the energy landscape becomes more rugged with many shallow minima. (b) Cross section of the energy landscape, corresponding to the extreme orientation of the RHH domains in the nonspecific or up-cis DNA binding state of NikR. (c) Different cross section of the energy landscape corresponding to an orientation in which the RHH domains adopt the specific or down-cis DNA binding state of NikR. Four energy minima are shown for the two DNA binding modes and represent four different DNA subsequences, i.e., four different sites on the DNA polymer.