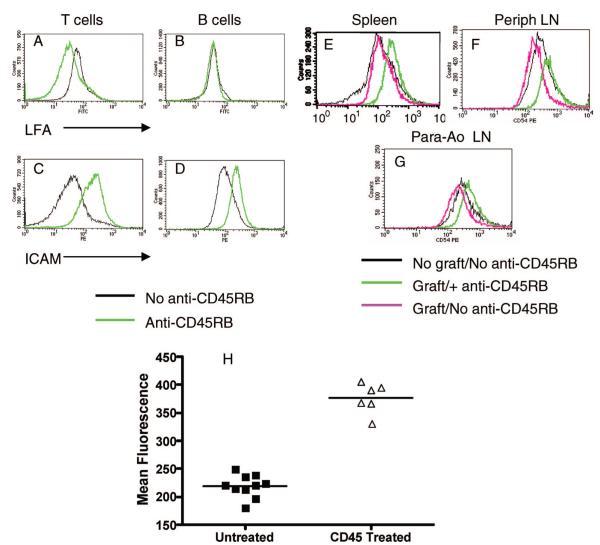
FIGURE 1.
Expression of CD54 by B lymphocytes after anti-CD45RB therapy. Naive B6 animals were given a routine course of anti-, and the expression of LFA-1 (A and B) and intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 (C and D) was analyzed on splenic T and B lymphocytes at the end of therapy. LFA-1 expression was down-regulated on T cells (CD3+, A) but B cell expression was unaffected (CD19+, B). ICAM-1 expression was enhanced on both splenic T (C) and B (D) lymphocytes. (E–F) B6 mice were grafted with allogeneic C3H hearts in the presence or absence of anti-CD45RB administered by the routine protocol. Exposure to anti-CD45RB leads to up-regulation of CD54 on B cells in multiple sites as identified by B220-gating. Up-regulation of B lymphocyte CD54 (ICAM-1) is detected in the spleen (E), peripheral nodes (F), and para-aortic lymph nodes (G). (H) Mean fluorescence intensities of anti-CD54 staining of splenic B lymphocytes from anti-CD45RB treated and untreated animals were compiled from four different experiments. A nearly twofold increase in MFI is seen consistently after anti-CD45RB therapy (P<0.0001, unpaired t test). Similar analysis for draining and para-aortic lymph nodes also reveals a significant increase in ICAM-1 expression (P<0.01, unpaired t test).