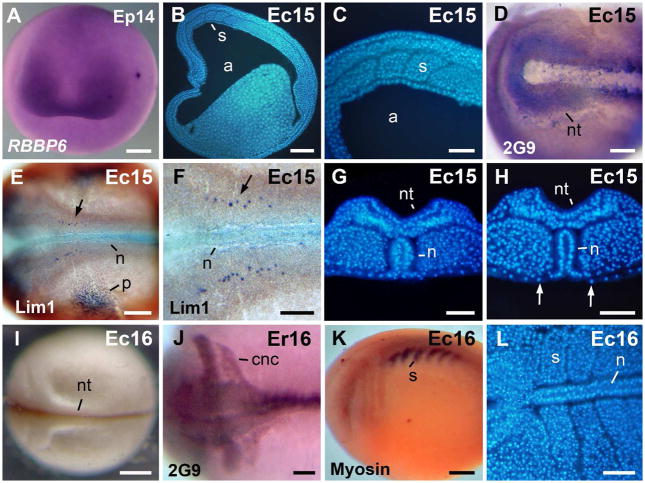
Fig. 4.
Morphology of the neurula. A: Neurula stage, anterior view, dorsal to the top. In situ hybridization signal of RBBP6 was detected in the presumptive eye region. B: Para-sagittal section through the somites. C: Higher magnification, of the embryo in B. D: The antigen 2G9-positive neural folds. E: The Lim1-positive notochord, cns cells, and pronephros anlage in a stage 15 embryo. F: Higher magnification of the embryo in E. The arrows in E–F signal a cns Lim 1-positive nucleus. G: Transversal section through the rostral region. The archenteron roof is covered by endoderm. H: Transversal section through the caudal region. The notochord is exposed in the gastrocoel roof plate. Arrows signal the lateral endodermal crests. I: A late neurula in dorsal view. J: The antigen 2G9-positive neural tube and cranial neural crest cell streams. K: Embryo immunostained against sarcomeric meromyosin (indicated as Myosin in the image). L: Horizontal section through the somites. Abbreviations: a, archenteron; cnc, cranial neural crest; n, notochord; nt, neural tube; p, pronephros anlage; s, somite. Scale bars: 100 μm in C,F–H, J,L; 200 μm in D,E; 250 μm in A,B,K; 400 μm in I.