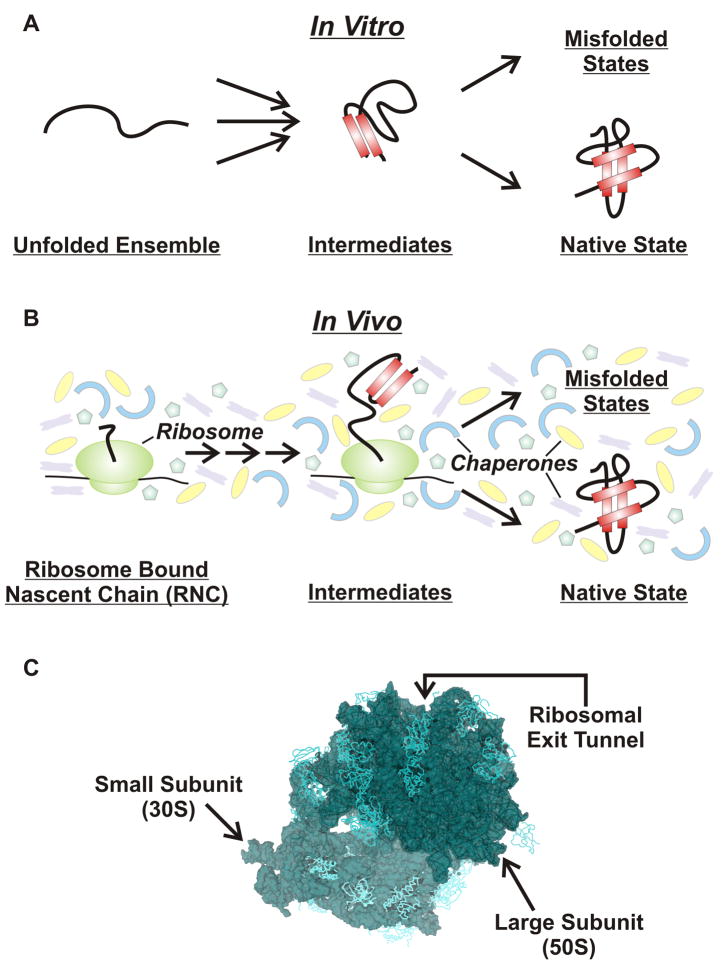
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of (A) in vitro and (B) in vivo protein folding pathways. Protein folding studies in vitro begin from a chemically or temperature induced unfolded ensemble and proceed through folding intermediates to either the native folded structure or misfolded/aggregated states. Protein folding in the cell differs from in vitro folding due to the influence of molecular chaperones, the ribosome and molecular crowding. (C) High resolution three-dimensional structure of the E. coli 70S ribosome (PDB codes 2AVY, 2AW4) [97].