Figure 5.
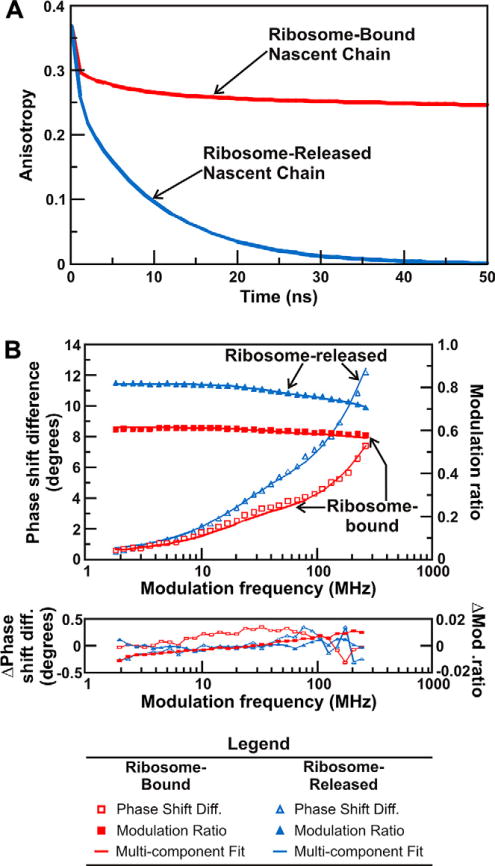
(A) Time-domain simulation illustrating the influence of the slow global tumbling of the ribosome on the observed anisotropy decay. Slow global tumbling prevents the anisotropy of ribosome-bound nascent chains from decaying to zero throughout the ns lifetime of the fluorophore. The anisotropy decays of nascent proteins released from the ribosome decay to zero within 50 ns. All simulations were performed with the Vinci software (ISS, Urbana Champaign). (B) Fluorescence depolarization raw data, multicomponent fits, and curve fitting residuals for ribosome-bound and ribosome-released full-length apoHmpH. The fit parameters derived from this FD anisotropy measurement are shown in Table 1.
