Fig. 6. Effects of the wild type and redox-negative forms of dPrx5 on JNK signaling.
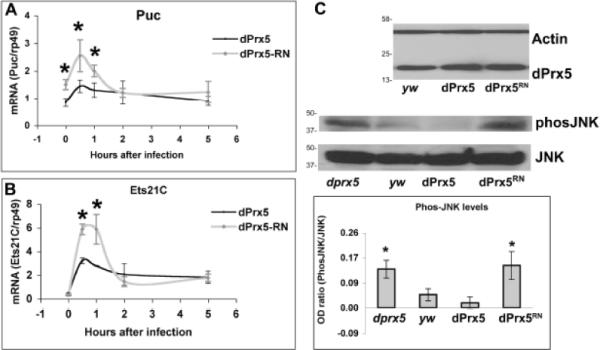
The expression of dPrx5 or dPrx5RN was achieved using corresponding UAS transgenes and dprx5 or recombinant Da-GAL4, dprx5 alleles. The genotype of the generated flies was yw; UAS-dPrx5(or dPrx5RN)/+; dprx5/Da-GAL4,dprx5. A and B, expression analysis of puckered and Ets21C, induced by bacterial infection. Total RNA was isolated from flies infected with E. coli at different time intervals. RT-PCR was performed with primers specific for Puckered and Ets21C and signals obtained were standardized against signals obtained for the housekeeping gene rp49. Statistically significant (P<0.05) differences are denoted by asterisks. C, Expression levels of wild type and redox-negative forms of dPrx5 protein are shown on the upper image. Phosphorylation of Basket in flies expressing wild type and redox-negative forms of dPrx5 are shown on the lower image. Proteins were isolated from control (y w), dprx5 mutant (dprx5) and flies expressing UAS-dPrx5 or UAS-dPrx5RN in dprx5 null background (indicated as dPrx5 and dPrx5RN) and resolved by PAGE electrophoresis. Immunoblot analysis was performed with anti-dPrx5 and anti-Actin antibodies to control for loading. Phosphorylated JNK (Basket) was detected with anti-phos-JNK antibodies and with anti-JNK antibodies as a control. Protein molecular weight markers (kDa) are indicated on the left. Intensity of the phos-JNK signals standardized against signals obtained for JNK is plotted on the graphs. The results are mean ± SD, n=3. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between the dprx5 mutant or flies expressing dPrx5RN and yw control and dPrx5-expressing flies.
