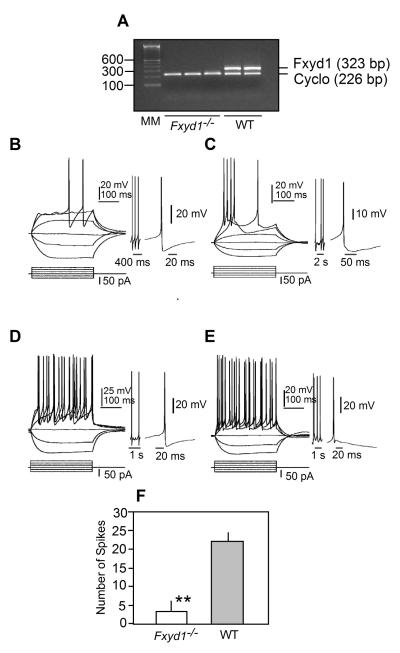
Figure 5.
Absence of Fxyd1 mRNA in the MBH of Fxyd1-/- mice and responses of GnRH neurones from Fxyd1-/- and WT female mice to somatic current pulse injections. All recordings were done under current clamp conditions and using 28-30 day-old female mice. A, Gel image of a semi-quantitative PCR reaction demonstrating the absence of Fxyd1 mRNA in the MBH of Fxyd1-/- female mice collected when the animals were 28 days of age. B, Response of a Fxyd1-/- GnRH neurone located in the central mPOA, C, Response of a Fxyd1-/- GnRH neurone located in the dorso-lateral mPOA, D, Response of a WT GnRH neurone in the central mPOA, E, Response of a WT dorso-lateral GnRH neurone. In each panel, the current pulse protocol is shown at the bottom and the responses at the top. Regardless of their Fxyd1 genotype, GnRH neurones of the central mPOA always showed an fAHP response after an evoked action potential. This is illustrated as expanded tracings to the right of panels B-E. The expanded tracing to the right of panels B and C show the fAHP response of Fxyd1-/- neurones located centrally (B) or dorso-laterally (C) in the mPOA. The expanded tracing to the right of panel D shows a dorso-lateral WT GnRH neurone exhibiting fAHP, and the tracing to the right of panel E depicts a dorso-lateral GnRH neurones lacking fAHP. F, Quantification of the number of action potentials elicited by current pulse injection in GnRH neurones from Fxyd1-/- (n=10) and WT (n=12) animals. The resting membrane potential is -60 mV in B, C, and E; -58 mV in D. **, p<0.01.