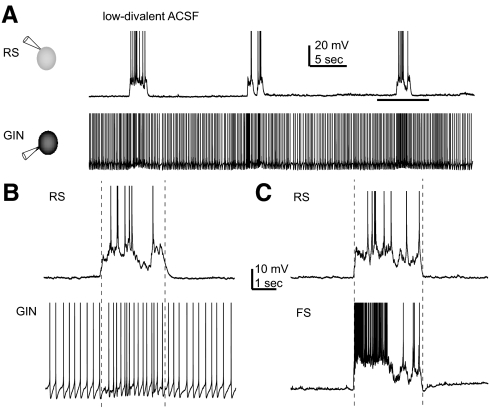
Fig. 1.
up- and down-states in regular spiking (RS), fast spiking (FS), and GFP- (and somatostatin-) expressing inhibitory neurons (GIN) cells. A: simultaneously recorded RS and GIN cells during application of low-divalent artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF). RS cells fired during up-states only, whereas GIN cells fired during both up- and down-states. B: period during horizontal line in A enlarged to show a single up-state in both cell types. C: up-state recorded in an FS cell and a different RS cell from that shown in A and B. In all 3 panels, action potentials are truncated for display purposes. Vertical dotted lines in B and C indicate start and end times of the up-states, as defined using the detection algorithm described in methods. In both cases, the RS cell was used to determine the up-state beginning and end.