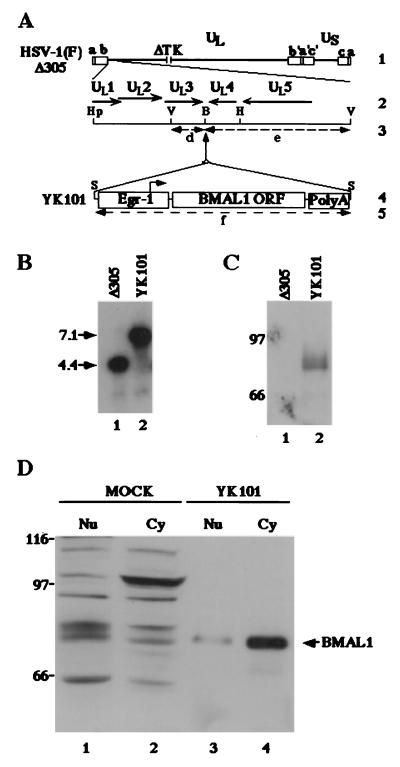
Figure 4.
(A) Schematic diagram of the sequence of HSV-1(F)Δ305 and the recombinant virus, YK101, derived from it. Line 1, sequence arrangement of the HSV-1(F)Δ305 DNA. Line 2, an enlarged portion of the domain of HSV-1 encoding UL1–UL5. The coding region and direction of the genes are indicated. Line 4, sequence of the recombinant virus, YK101, which was selected, as described in Materials and Methods, from among the progeny of transfection of rabbit skin cells with intact HSV-1(F)Δ305 DNA and plasmid pBMAL1 in UL3–4. The promoter sequence of Egr-1, the BMAL1 coding sequence, and the sequence containing bidirectional poly(A) signals of UL21 and UL22 of HSV-1(F) are shown as open rectangles. The arrow indicates the site of transcription initiation and direction of transcription. Lines 3 and 5 show expected sizes of DNA fragments generated by cleavage of the DNA. The fragment designations shown here are identical to those described in the text and in B. Restriction sites: B, BamHI site; Hp, HpaI site; S, SphI site; and V, EcoRV. (B) Characterization of an HSV-1 recombinant virus expressing the BMAL1 gene (YK101). Autoradiographic image of electrophoretically separated EcoRV digests of HSV-1(F)Δ305 or YK101 DNAs, hybridized to the radiolabeled EcoRV-HindIII fragment of pRB442 that contained sequences of UL3 and UL4. (C) Lane 1, digest of DNA of HSV-1(F)Δ305. Lane 2, digest of DNA of recombinant virus YK101. Molecular weights (×1,000) are shown on the left. (D) Photographic image of an immunoblot of electrophoretically separated lysates of HSV-1(F)Δ305 (lane 1) or YK101 (lane 2) infected with Vero cells harvested 24 h after infection. The blot was probed with the anti-BMAL1 polyclonal antibody. Molecular weights (×1,000) are shown on the left. (D) Photographic image of an immunoblot of electrophoretically separated cell fractions of SK-N-SH cells mock-infected (lanes 1 and 2) or infected with YK101 (lanes 3 and 4). Nuclear (Nu; lanes 1 and 3) and cytoplasmic (Cy; lanes 2 and 4) fractions of infected SK-N-SH cells harvested 24 h after infection were prepared as described in Materials and Methods and reacted with the anti-BMAL1 polyclonal antibody. BMAL1-specific band is indicated on the right, and molecular weights (×1,000) are shown on the left.