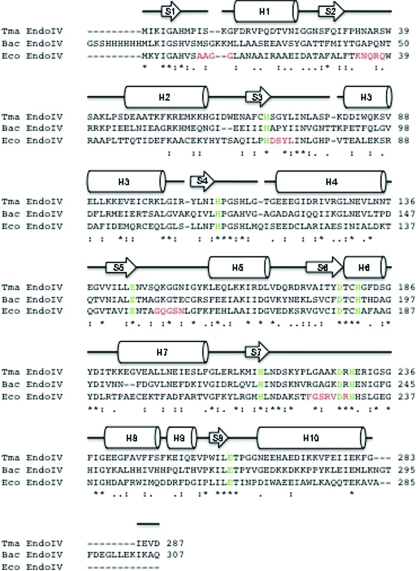
Figure 3.
Amino-acid sequence alignment of T. maritima endonuclease IV (287 residues), E. coli endonuclease IV (285 residues) and Bacillus anthracis endonuclease IV (307 residues). The amino-acid sequences of T. maritima endonuclease IV (Tma EndoIV; Q9WYJ7), E. coli endonuclease IV (Eco EndoIV; P0A6C1) and B. anthracis endonuclease IV (Bac EndoIV; Q81LV1) from PDB code 1xp3 (M. J. Fogg, V. M. Levdikov, E. V. Blagova, J. A. Brannigan, A. J. Wilkinson & K. S. Wilson, unpublished work) were aligned with the program ClustalW (Thompson et al., 1994 ▶). The secondary-structure elements of T. maritima endonuclease IV bound to zinc are shown aligned with its primary sequence, where H and S represent α-helices and β-sheets, respectively. The absolutely conserved amino-acid residues in the active-site regions of Tma EndoIV, Eco EndoIV and Bac EndoIV that are involved in the binding of divalent metal ions are colored green. The five R-loop regions (residues 10–13, 34–38, 70–73, 149–153 and 224–230) in E. coli endonuclease IV that have been shown to be involved in DNA binding are colored in red below the corresponding residues in both T. maritima endonuclease IV and B. anthracis endonuclease IV. The ‘*’ symbol indicates identical residues in the sequence alignment, the ‘:’ symbol indicates conserved substitutions in the sequence alignment and the ‘.’ symbol indicates semi-conserved substitutions in the sequence alignment.