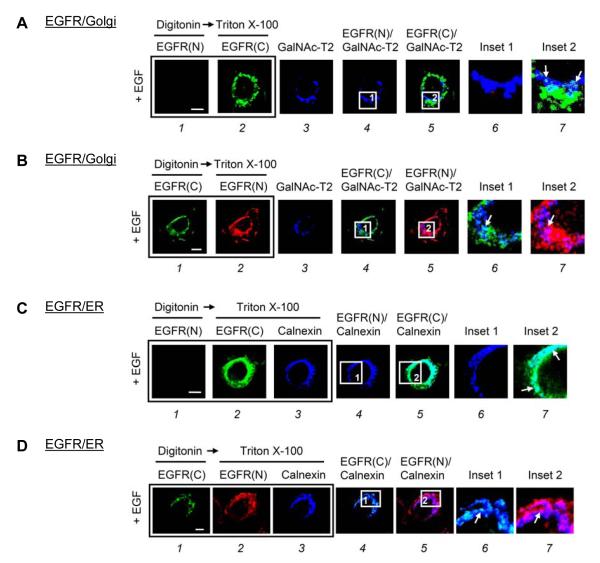
Fig. 1. The NH2-terminus of EGFR resided within the Golgi and ER lumen after EGF treatment in MDA-MB-468 cells.
(A and B) MDA-MB-468 cells transfected with GalNAc-T2-GFP as a Golgi marker were treated with EGF for 15 min. (C and D) MDA-MB-468 cells maintained in serum-starved medium for 24 h were treated with EGF for 30 min. Cells were then immunostained with the indicated antibodies in a triple-labeled assay and analyzed using confocal microscopy. Briefly, after fixation, the cells were permeabilized with digitonin and incubated with the first primary antibodies: (A-1 and C-1) mouse anti-NH2-terminal EGFR(N), and (B-1 and D-1) rabbit anti-COOH-terminal EGFR(C) antibodies. Subsequently, the cells were refixed and permeabilized with Triton X-100 to the second and third primary antibodies: (A-2 and C-2) EGFR(C), (B-2 and D-2) EGFR(N), and (C-3 and D-3) goat anti-calnexin antibodies. The boxed areas are shown in detail in the insets. Bar, 5 μm.