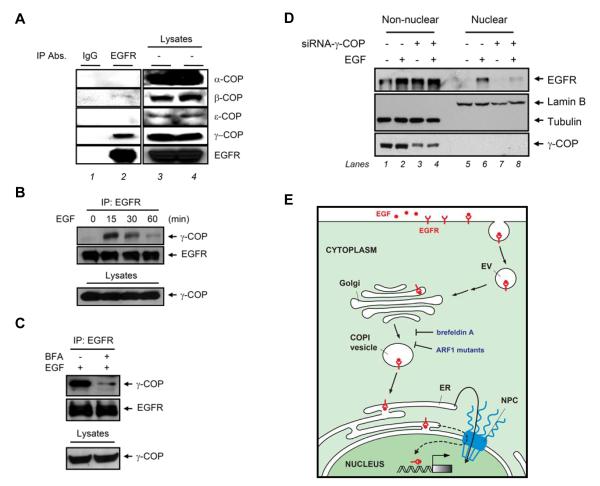
Fig. 4. COPI-mediated retrograde trafficking from the Golgi to the ER regulates EGF-dependent EGFR nuclear transport.
(A) Analysis of EGF-dependent association of EGFR with COP subunits. Total lysates from MDA-MB-468 cells treated with EGF were immunoprecipitated with anti-EGFR antibodies and subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Immunoprecipitation performed with IgG was used as a negative control. Protein expression levels were duplicated. (B) EGFR associated with γ-COP in response to EGF. (C) Pretreatment with BFA inhibited the association of EGFR and γ-COP by EGF treatment for 15 min. (D) Knockdown of γ-COP expression by γ-COP siRNA downregulated EGF-dependent EGFR nuclear translocation in HeLa cells. (E) Diagram of retrograde trafficking from the Golgi to the ER transport by EGF treatment. The scale of the diagram does not reflect the relative sizes of different molecules or subcellular structures. The dashed lines linking the ER and the nucleus are based on postulate from a previous report [26]. EV, endocytic vesicle; COPI, coat protein complex I; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; NPC, nuclear pore complex.