Abstract
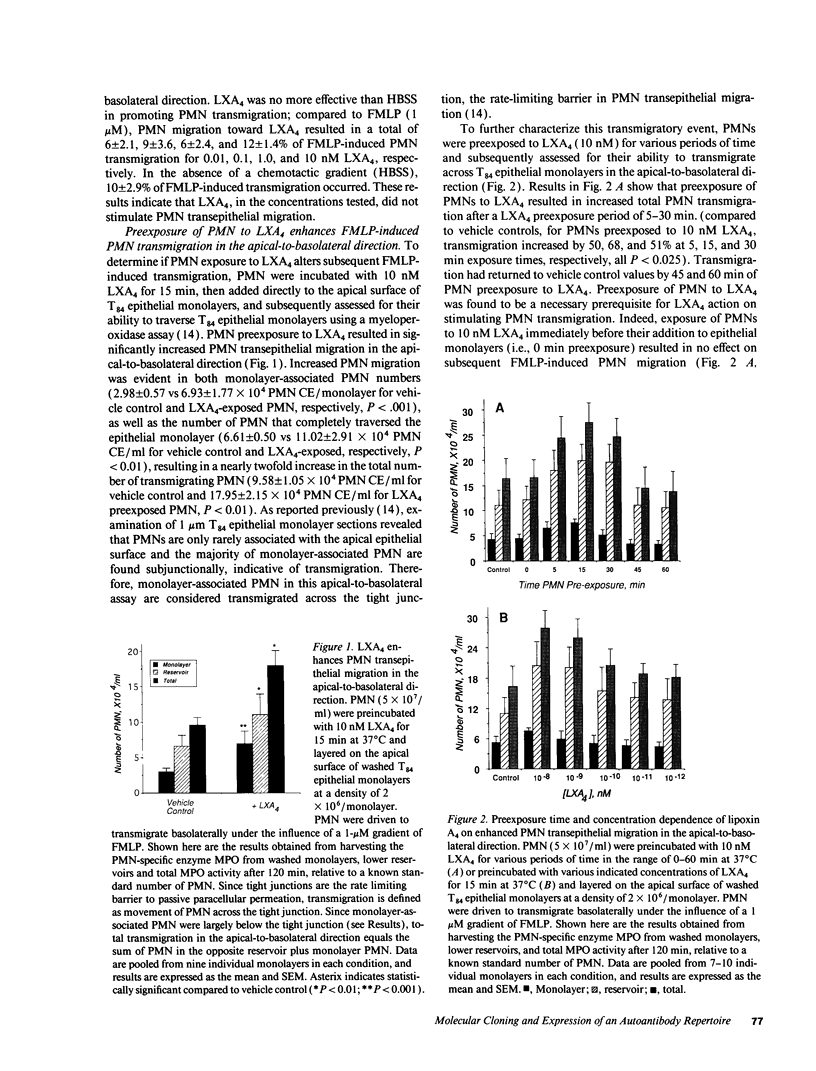
Neutrophil (PMN) migration across intestinal epithelial barriers, such as occurs in many disease states, results in modifications in epithelial barrier. Here, we investigated the impact of lipoxin A4 (LXA4), an eicosanoid with counterregulatory inflammatory roles, on PMN migration across cultured monolayers of the human intestinal epithelial cell line T84. Transepithelial migration of PMN was assessed in the apical-to-basolateral direction and in the basolateral-to-apical direction. In the apical-to-basolateral direction, preexposure of PMN to LXA4 (10 nM, 15 min) stimulated an 87 +/- 5% increase in transepithelial migration of PMN as determined by a PMN myeloperoxidase assay. The LXA4-elicited effect on transmigration was present throughout the 2-h assay period and was not secondary to LXA4 effects on epithelial monolayer integrity as judged by measurement of transepithelial resistance. PMN migration in the basolateral-to-apical direction was modulated by LXA4 with a comparable time- and concentration-dependence to that in the apical-to-basolateral direction. However, qualitative differences in how LXA4 modulates transmigration in the two opposing directions were observed. In the basolateral-to-apical direction, preexposure of PMN to LXA4 (10 nM, 15 min) diminished PMN transepithelial migration by 33 +/- 4%. Structure-function studies revealed that LXA4 and 11-trans-LXA4 (50% of LXA4 effect), but not LXB4, inhibited basolateral-to-apical PMN transmigration. The action of LXA4 was not sensitive to inhibitors of cyclooxygenase or specific leukotriene biosynthesis, but was sensitive to staurosporine, a protein kinase C inhibitor. These results suggest that migration of PMN across epithelia in the physiological direction may be qualitatively different following PMN exposure to eicosanoids. We propose that such retention of PMN at this specific anatomic location may serve an important role in mucosal defense.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaout M. A., Lanier L. L., Faller D. V. Relative contribution of the leukocyte molecules Mo1, LFA-1, and p150,95 (LeuM5) in adhesion of granulocytes and monocytes to vascular endothelium is tissue- and stimulus-specific. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Nov;137(2):305–309. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badr K. F., DeBoer D. K., Schwartzberg M., Serhan C. N. Lipoxin A4 antagonizes cellular and in vivo actions of leukotriene D4 in rat glomerular mesangial cells: evidence for competition at a common receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3438–3442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughton-Smith N. K., Hawkey C. J., Whittle B. J. Biosynthesis of lipoxygenase and cyclo-oxygenase products from [14C]-arachidonic acid by human colonic mucosa. Gut. 1983 Dec;24(12):1176–1182. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.12.1176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady H. R., Persson U., Ballermann B. J., Brenner B. M., Serhan C. N. Leukotrienes stimulate neutrophil adhesion to mesangial cells: modulation with lipoxins. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 2):F809–F815. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.5.F809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezinski D. A., Nesto R. W., Serhan C. N. Angioplasty triggers intracoronary leukotrienes and lipoxin A4. Impact of aspirin therapy. Circulation. 1992 Jul;86(1):56–63. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C. Leukocyte-endothelial cell recognition: three (or more) steps to specificity and diversity. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1033–1036. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie P. E., Spur B. W., Lee T. H. The effects of lipoxin A4 on airway responses in asthmatic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jun;145(6):1281–1284. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.6.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgan S. P., Parkos C. A., Delp C., Arnaout M. A., Madara J. L. Neutrophil migration across cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers is modulated by epithelial exposure to IFN-gamma in a highly polarized fashion. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):785–798. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer E. B., Milks L. C., Brontoli M. J., Ojakian G. K., Wright S. D., Showell H. J. Effect of human serum and some of its components on neutrophil adherence and migration across an epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1868–1877. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Madara J. L. Established intestinal cell lines as model systems for electrolyte transport studies. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:354–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92082-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. W., Taylor J. E., Walker J. D., Simmons N. L. Transepithelial chemotaxis of rat peritoneal exudate cells. Br J Exp Pathol. 1983 Dec;64(6):644–654. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiore S., Ryeom S. W., Weller P. F., Serhan C. N. Lipoxin recognition sites. Specific binding of labeled lipoxin A4 with human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16168–16176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard J., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Chan C., Charleson S., Denis D., Foster A., Fortin R., Leger S., McFarlane C. S., Morton H. L-663,536 (MK-886) (3-[1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-t-butyl-thio-5-isopropylindol-2-yl]-2,2 - dimethylpropanoic acid), a novel, orally active leukotriene biosynthesis inhibitor. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1989 May;67(5):456–464. doi: 10.1139/y89-073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandordy B. M., Lacroix H., Mavoungou E., Krilis S., Crea A. E., Spur B. W., Lee T. H. Lipoxin A4 inhibits phosphoinositide hydrolysis in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1022–1029. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90625-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawker P. C., McKay J. S., Turnberg L. A. Electrolyte transport across colonic mucosa from patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1980 Sep;79(3):508–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., Raud J., Palmertz U., Haeggström J., Nicolaou K. C., Dahlén S. E. Lipoxin A4 inhibits leukotriene B4-induced inflammation in the hamster cheek pouch. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989 Dec;137(4):571–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1989.tb08805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh T., Takahashi K., DeBoer D. K., Serhan C. N., Badr K. F. Renal hemodynamic actions of lipoxins in rats: a comparative physiological study. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 2):F436–F442. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.3.F436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson R. S., Springer T. A. Structure and function of leukocyte integrins. Immunol Rev. 1990 Apr;114:181–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Horton C. E., Kyan-Aung U., Haskard D., Crea A. E., Spur B. W. Lipoxin A4 and lipoxin B4 inhibit chemotactic responses of human neutrophils stimulated by leukotriene B4 and N-formyl-L-methionyl-L-leucyl-L-phenylalanine. Clin Sci (Lond) 1989 Aug;77(2):195–203. doi: 10.1042/cs0770195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Lympany P., Crea A. E., Spur B. W. Inhibition of leukotriene B4-induced neutrophil migration by lipoxin A4: structure-function relationships. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 14;180(3):1416–1421. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Dharmsathaphorn K. Occluding junction structure-function relationships in a cultured epithelial monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2124–2133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J., Dharmsathaphorn K., Carlson S. Structural analysis of a human intestinal epithelial cell line. Gastroenterology. 1987 May;92(5 Pt 1):1133–1145. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(87)91069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliorisi G., Folkes E., Cramer E. B. Differences in the ability of neutrophils and monocytes to traverse epithelial occluding junctions. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Dec;44(6):485–492. doi: 10.1002/jlb.44.6.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakadate T., Yamamoto S., Aizu E., Nishikawa K., Kato R. H-7, a protein kinase C inhibitor, inhibits phorbol ester-caused ornithine decarboxylase induction but fails to inhibit phorbol ester-caused suppression of epidermal growth factor binding in primary cultured mouse epidermal cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;36(6):917–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash S., Parkos C., Nusrat A., Delp C., Madara J. L. In vitro model of intestinal crypt abscess. A novel neutrophil-derived secretagogue activity. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1474–1477. doi: 10.1172/JCI115156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash S., Stafford J., Madara J. L. Effects of polymorphonuclear leukocyte transmigration on the barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1104–1113. doi: 10.1172/JCI113167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S., Fiore S., Luscinskas F. W., Serhan C. N. Lipoxin A4 and lipoxin B4 stimulate the release but not the oxygenation of arachidonic acid in human neutrophils: dissociation between lipid remodeling and adhesion. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jun;143(3):512–523. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041430316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L. Leukocyte adhesion to endothelium in inflammation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90230-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmblad J., Gyllenhammar H., Ringertz B., Serhan C. N., Samuelsson B., Nicolaou K. C. The effects of lipoxin A and lipoxin B on functional responses of human granulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):168–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Colgan S. P., Delp C., Arnaout M. A., Madara J. L. Neutrophil migration across a cultured epithelial monolayer elicits a biphasic resistance response representing sequential effects on transcellular and paracellular pathways. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(4):757–764. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.4.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Delp C., Arnaout M. A., Madara J. L. Neutrophil migration across a cultured intestinal epithelium. Dependence on a CD11b/CD18-mediated event and enhanced efficiency in physiological direction. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1605–1612. doi: 10.1172/JCI115473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Cotran R. S. The role of endothelial cells in inflammation. Transplantation. 1990 Oct;50(4):537–544. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199010000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sako T., Tauber A. I., Jeng A. Y., Yuspa S. H., Blumberg P. M. Contrasting actions of staurosporine, a protein kinase C inhibitor, on human neutrophils and primary mouse epidermal cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4646–4650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Dahlén S. E., Lindgren J. A., Rouzer C. A., Serhan C. N. Leukotrienes and lipoxins: structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1171–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.2820055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon P., Stenson W. F. Enhanced synthesis of leukotriene B4 by colonic mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Mar;86(3):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard K. A., Greenberg S. M., Funk C. D., Romano M., Serhan C. N. Lipoxin generation by human megakaryocyte-induced 12-lipoxygenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jan 13;1133(2):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teahon K., Smethurst P., Pearson M., Levi A. J., Bjarnason I. The effect of elemental diet on intestinal permeability and inflammation in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jul;101(1):84–89. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90463-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley J. H., Donowitz M. Colo-rectal biopsy in inflammatory bowel disease. Monogr Pathol. 1977;(18):50–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








