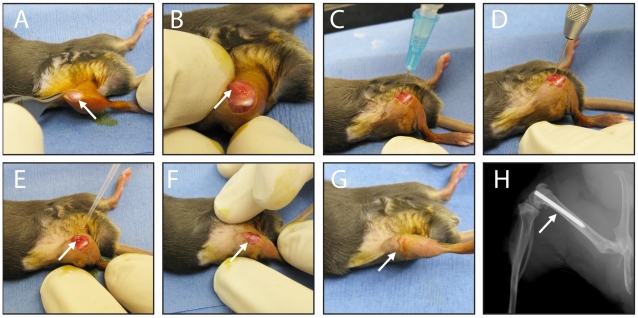
Figure 1. Mouse surgical procedures.
(A) An incision was made in the skin overlying the right knee joint (arrow). (B) A medial parapatellar arthrotomy with lateral displacement of the quadriceps-patellar complex was performed to locate the intercondylar femoral notch (arrow). (C) An intramedullary canal was manually reamed into the distal femur with a 25 gauge needle. (D) An orthopaedic-grade stainless steel K-wire (diameter 0.6 mm) was surgically placed in a retrograde fashion into the intramedullary canal and cut so that the cut end extended 1 mm into the joint space. (E) An inoculum of S. aureus in a 2 µl volume was pipetted into the joint space (arrow). (F) The quadriceps-patellar complex was reduced back to the midline (arrow) and (G) the surgical site was closed with subcutaneous 5-0 Dexon sutures (arrow). (H) A representative radiographic image demonstrating the placement of the implant in the femoral canal with the cut end extending into the knee joint.