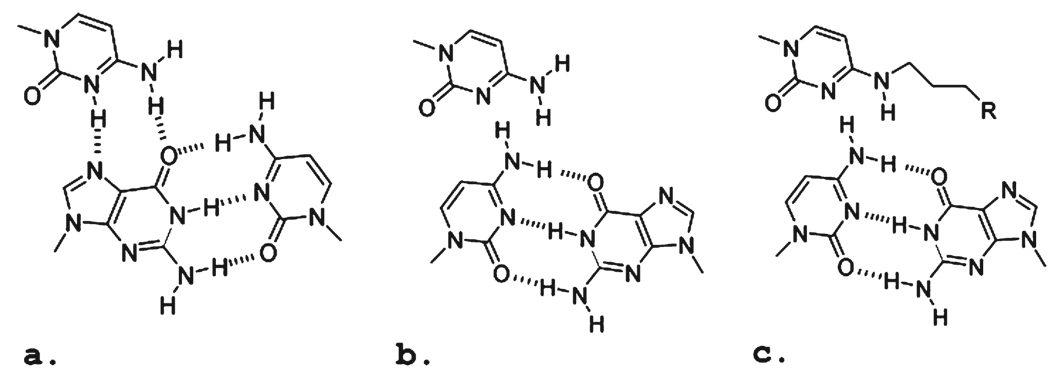
FIGURE 1.
Schematic of base triplets formed in either an uninterrupted polypurine:polypyrimidine sequence or one with an “inverted” interruption in the sequence: (a) canonical G:C·C+, (b) inverted C:G·C, and (c) inverted C:G·Cmod. The R group is designed to afford additional hydrogen bonding between the base analogue and the purine base of the inverted base in the duplex target sequence.