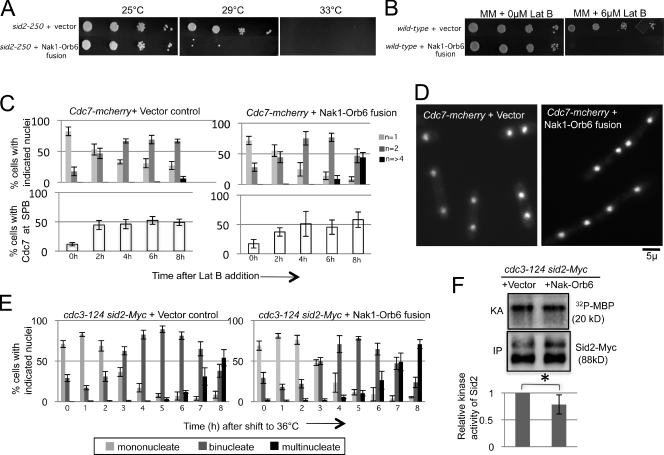
Figure 4.
MOR inhibition becomes essential when cytokinesis is perturbed. (A) sid2-250 cells expressing the vector alone or the Nak1–Orb6 fusion transgene were grown in medium lacking thiamine for 14 h at 25°C to induce expression of the fusion protein before spotting 10-fold serial dilutions on minimal media plates lacking thiamine at the indicated temperatures. (B) Wild-type cells carrying the indicated plasmids were grown as in A and then 10-fold serial dilutions were spotted on minimal media plates with or without 6 µM Lat B and tested for growth at 25°C. (C) Wild-type cells carrying integrated copies of Cdc7-mcherry were transformed with the indicated plasmids, and grown as in A for 19 h before being treated with a low dose (4 µM) of Lat B. Samples were collected every 2 h for 8 h after drug addition (0 h). Cells were fixed, stained with DAPI, and scored for number of nuclei (n, top panel) and Cdc7 localization at the SPB (bottom panel). At least 100 cells were analyzed for nuclei count and at least 50 for scoring Cdc7-mcherry localization. Error bars denote SD for three separate experiments. (D) Representative images of the Cdc7-mcherry cells expressing vector alone or the Nak1–Orb6 fusion at the 7-h time point are shown. (E) cdc3-124 sid2-13Myc cells expressing either the empty vector control or the fusion protein were grown in media lacking thiamine for 19 h at 25°C and then shifted to 36°C. Samples were collected for DAPI stain and nuclei count every hour for 8 h after shift to 36°C. Error bars denote SD for three separate experiments. (F) Cells with the indicated genotypes were grown as in E and shifted to 36°C for 3 h. Cell extracts were prepared and Sid2-13Myc was immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) antibody. The immunoprecipitates were split, with one portion used for Western blotting using Myc antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) (IP) and the other portion used for in vitro kinase assays using myelin basic protein (MBP; Sigma-Aldrich) as an artificial substrate as described previously (Sparks et al., 1999) and in Materials and methods. The kinase activity (KA) was measured using a PhosphorImager (MDS Analytical Technologies), quantified using ImageQuant software, and normalized to the amount of Sid2 (IP). The activity relative to cells with the control plasmid is shown. Error bars denote SD of the relative KA. The difference in Sid2 kinase activity between cells expressing the vector and those expressing the fusion protein was not statistically significant based on t test analysis from three different experiments. *, P = 0.1047.