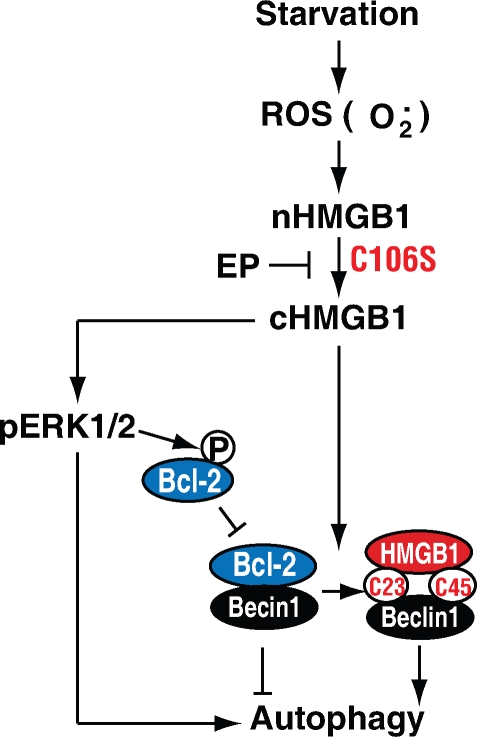
Figure 8.
Conceptual relationships between endogenous HMGB1 and autophagy. ROS trigger HMGB1 translocation to the cytosol in the setting of starvation-mediated autophagy. Cytosolic HMGB1 then binds Beclin1, which requires C23/45. This results in dissociation of Beclin1–Bcl-2 and subsequent induction of autophagy. C106 mutation (C106S) in HMGB1 impairs its nuclear localization and promotes autophagy. Inhibition of HMGB1 translocation by ethyl pyruvate (EP) blocks autophagy. Additionally, HMGB1 promotes phosphorylation and activation of the ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2) pathway, which is an important autophagy-dependent signal pathway.