Figure 4.
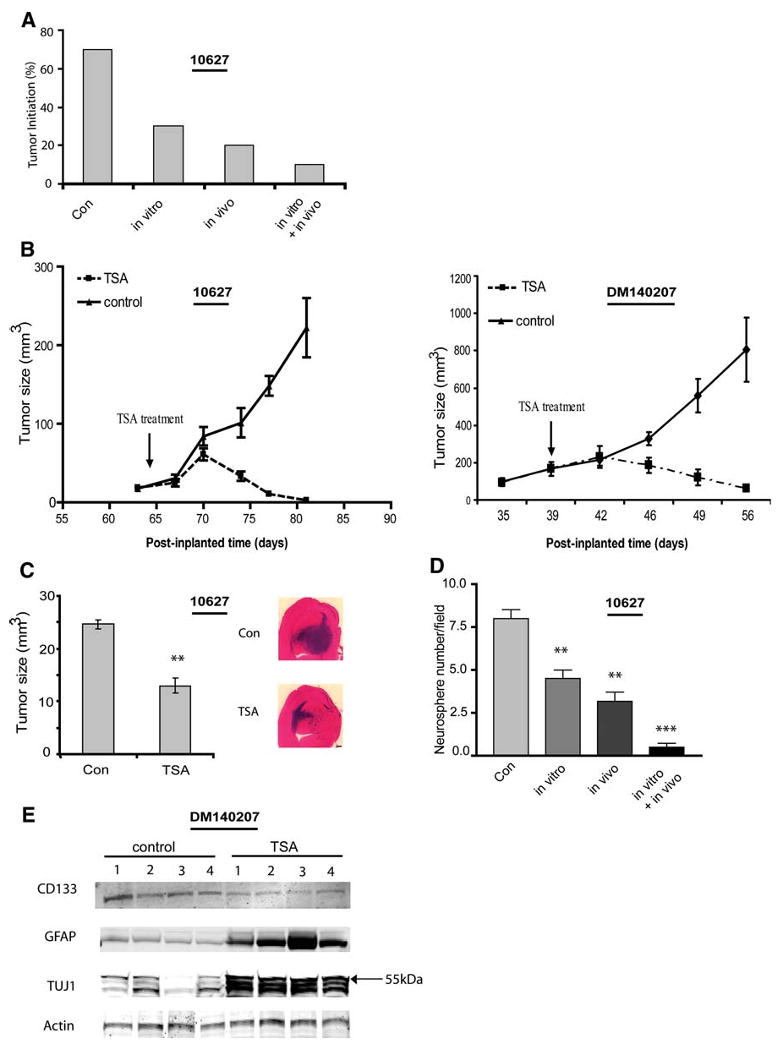
HDAC inhibitors reduce tumor propagation by GBM-derived neurospheres and deplete tumor xenografts of neurosphere-forming stem-like cells. (A): GBM-derived neurospheres were treated with or without TSA (200 nM) for 4 days in vitro. Equal numbers of viable cells (5 × 106) were implanted s.c. to Nu/nu mice (n = 10) and animals began treatment with or without TSA (0.5 mg/kg per day i.p.) 5 days after cell implantation. The percentage of tumors formed over 8 weeks was quantified. Seventy percent of controls (buffer-treated only) formed tumors. Transient exposure to TSA before cell implantation (in vitro) reduced tumor propagation to 30%. Tumor propagation was further inhibited by in vivo TSA. (B): When mice bearing pre-established s.c. xenografts (∼50 mm3) were treated with TSA (0.5 mg/kg per day i.p.) the tumors (n = 6) regressed within 10 days of treatment initiation. (C): GBM-derived neurospheres were treated for 4 days with or without TSA (200 nM) in vitro. Viable neurosphere cells (5 × 103) were then implanted to the caudate/putamen. After 6 weeks, the mice were sacrificed. Histological analysis revealed that tumor propagation rates by control- and TSA-treated neurosphere cells were 80% and 50%, respectively. Tumors propagated by TSA-treated neurospheres were significantly smaller than tumors derived from control neurospheres (p < .01). (D): s.c. xenografts were established from GBM-derived neurospheres as in (A). After 8 weeks in vivo, xenografts were dissected and equal numbers of dissociated cells were used to establish primary cultures in neurosphere growth medium. Neurospheres formed after one passage were immobilized in agar and those measuring >100 μm diameter were quantified by computer-assisted morphometry as described in Figure 1. All TSA treatment conditions depleted the tumor xenografts of neurosphere-forming stem-like cells. (E): Nu/nu mice bearing GBM xenografts derived from neurosphere cells were treated with TSA as described in (B). After 19 days of treatment, residual tumors were resected and whole tumor protein extracts were assayed for GFAP, TuJ1, CD133, and actin by immunoblot analysis. TSA therapy in vivo decreased tumor expression of CD133 and increased tumor expression of differentiation markers. Note that, in whole tumor protein extracts, anti-TuJ1 identified approximately three species at and below 55 kDa. Data are shown as the mean ± standard error of the mean. (B–D). **p < .01 and ***p < .001, compared with controls. Abbreviations: Con, control; GBM, glioblastoma; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; HDAC, histone deacetylase; TSA, trichostatin A.
