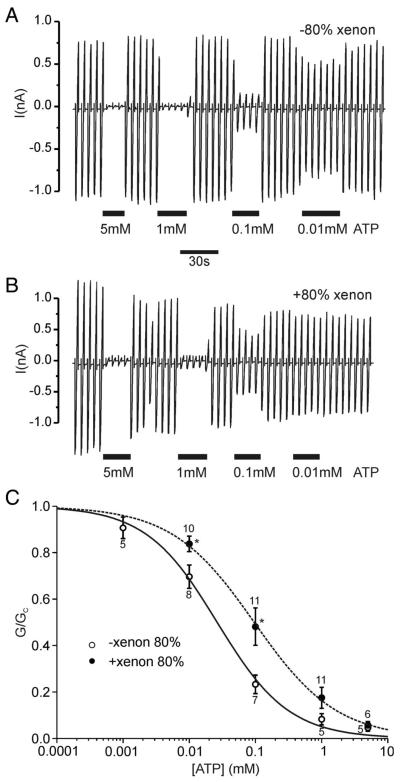
Fig. 5.
Xenon reduces ATP inhibition of inside-out patches. (A, B) Inside-out patch-clamp recordings of Kir6.2/SUR1 currents in the absence (A) or presence (B) of 80% xenon. Recordings were performed in Mg2+-free solution (note the absence of refreshment) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) was applied as indicated by the bars. (C) ATP concentration–inhibition curves for Kir6.2/SUR1 currents in the absence of MgCl2 as obtained from experiments as shown in A and B. Experiments were performed either in the absence (open circles) or in the presence of 80% xenon (filled circles). Solutions containing ATP were alternated with ATP-free solutions. Slope conductance (G) in the presence of the drug is expressed as a fraction of the slope conductance in its absence (Gc). The dotted lines and solid lines are the best fit to the data using the modified Hill equation (Eq. 1). Numbers (N) are given above the data points. *P < 0.05 compared with same ATP concentration in the absence of xenon.