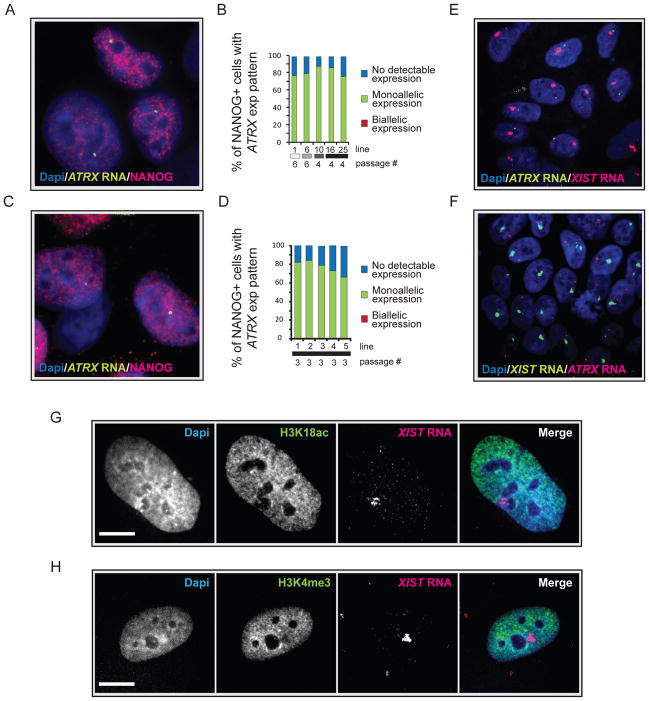
Figure 3. The XIST RNA- coated chromosome is inactive in female hiPSCs.
(A) NANOG immunostaining (red) combined with RNA FISH for ATRX nascent transcripts (green) in the Dapi-stained STEMCCA-hiPSC line 19. A pinpoint of ATRX marks the site of nascent transcription and occurs from only one X chromosome.
(B) The graph depicts the quantification of NANOG-positive cells with monoallelic, biallelic, or no ATRX expression for various STEMCCA-hiPSC lines at the indicated passage. Fibroblast origin is given as in Fig 2C.
(C) As in (A) for MIP-hiPSC line 1.
(D) As in (B) for various MIP-hiPSC lines.
(E) FISH for XIST RNA (red) and ATRX transcripts (green) in STEMCCA-hiPSC line G at passage 8 with Dapi staining the nucleus. The XIST RNA cloud signal does not overlap with the single ATRX signal.
(F) As in (E) for MIP-hiPSC line 5 at passage 3 with XIST RNA in green and ATRX transcripts in red.
(G) Immunostaining for H3K18ac (green) and FISH for XIST RNA (red) in STEMCCA-hiPSC line E at passage 8. Exclusion of the histone mark can be seen at the site of XIST RNA accumulation and was found in 96% of cells in the population indicating silencing of the entire XIST RNA-coated X in hiPSCs. Scale bar = 5um.
(H) As in (G), except that Xi exclusion of H3K4 me3 was analyzed. Exclusion of this histone mark was found in 92% of hiPSCs. See Fig S3 for additional data.