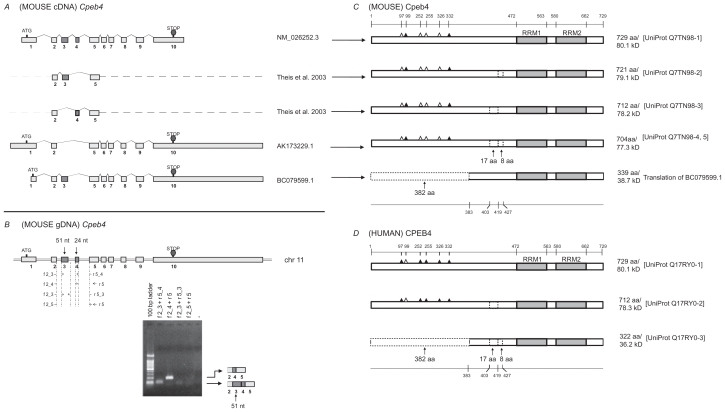
Figure 4.
Analysis of Cpeb4. A) Transcripts of mouse Cpeb4. Three non-redundant full-length UniGene sequences were used for this analysis, with the accession numbers listed on the right. ATG and STOP indicate the presence of translational initiation and termination sites, respectively. Partial sequences of two transcripts are derived from a previous publication.5 The different lengths of the first and the last exons likely represent the presence of different 5′ UTR and 3′ UTR, respectively. The alternative splices of exon 3 (51-nt) or exon 4 (24-nt) would generate different protein products. A shorter first exon leads to an alternative translational initiation site in BC079599.1. B) Expression of Cpeb4 transcripts in the adult mouse retina. The locations of the primers for RT-PCR are aligned to the diagram of Cpeb4 genomic DNA, in which boxes represent exons and double lines represent introns. The photograph of DNA Gel demonstrates the expression of multiple Cpeb4 transcripts in the retina with and without the exon 3. The identity of each band was confirmed by nucleotide sequencing. C) Isoforms of mouse Cpeb4 proteins. Four isoforms were extracted from the UniProt database. The computational translation of cDNA BC079599.1 would generate an additional isoform. RRMs are indicated with gray boxes. Triangles represent phosphorylation sites experimentally confirmed (solid)21,23 or predicted (open) based on cross-paralog comparisons, respectively. A 17-aa deletion, an 8-aa deletion, and a 382-aa N-terminal truncation are each indicated with dashed line boxes. The locations of functional motifs are shown as numbered amino acid sites at the top, and those of the alternative spliced regions at the bottom, as might be seen in the longest isoform. D) Isoforms of human CPEB4 proteins. Three isoforms are extracted from the UniProt database. The RRMs, the phosphorylation sites, the deletions and the truncation are all present in human CPEB4 at the same locations. All numerical locations refer to the longest isoform.