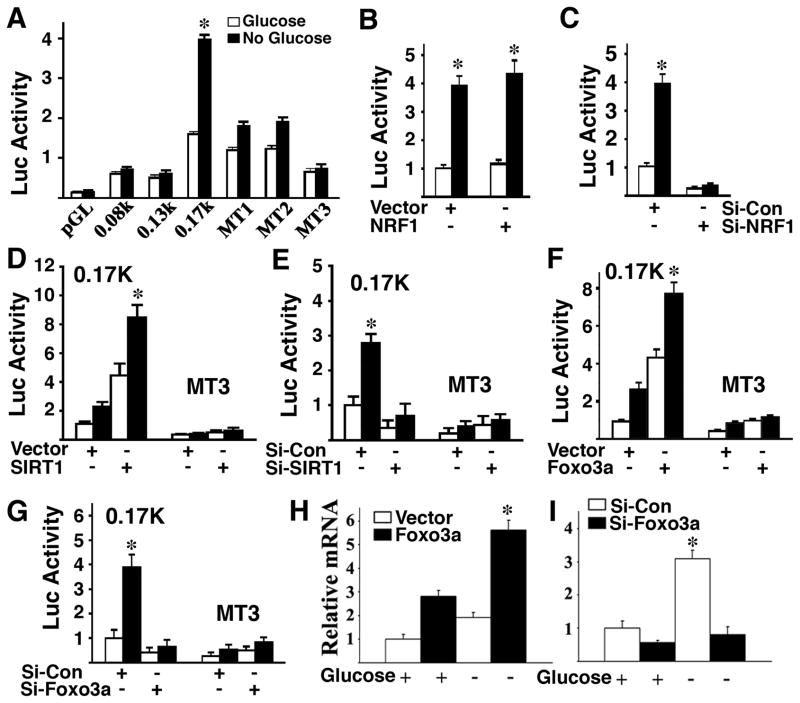
Fig. 2. Regulation of SIRT6 by SIRT1, FOXO3a, and NRF1.
(A) Absence of glucose in Hepa1-6 cells induced luciferase activity of a SIRT6 promoter reporter, while mutation of NRF1 binding sites abolished the induction. (B,C) Effect of NRF1 ectopic expression (B) and RNAi-mediated knockdown (C) on a SIRT6 promoter reporter. (D,E) Ectopic expression of SIRT1 increased SIRT6 promoter activity in the presence or absence of glucose (D), while mutation of NRF1 binding sites (D), or RNAi-mediated knockdown of SIRT1 (E) abolished the induction. (F,G) Ectopic expression of FOXO3a increased SIRT6 promoter activity in the presence or absence of glucose (F), while RNAi-mediated knockdown of FOXO3a inhibits it (G). (H,I) Absence of glucose induces expression of SIRT6 mRNA, which is further increased by overexpression of FOXO3a (H), while RNAi-mediated knockdown of FOXO3a abolished the induction (I).