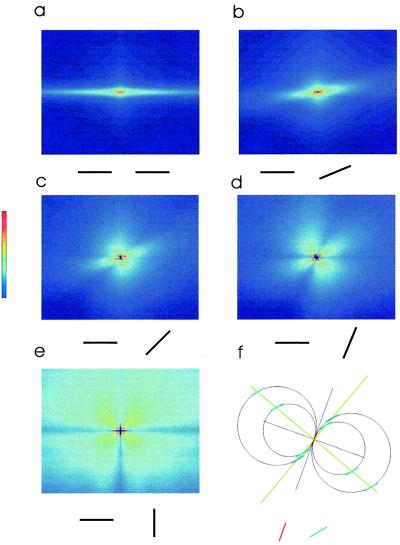
Figure 4.
Plot of the spatial dependence of the histogram of cooccurring pairs for different geometrical configurations. (a) The probability of finding a pair of iso-oriented segments as a function of their relative position; a pair of segments at relative orientation of 22.5° (b), 45° (c), 67.5° (d), or 90° (e). (f) Cocircularity solution for a particular example of two segments. The solutions to the problem of cocircularity are two orthogonal lines, whose main have values (ψ + ϕ)/2 or (ψ + ϕ + π)/2. For the example given, ϕ (red segment) = 20°, ψ (blue segment) = 40°, and the two solutions (green lines) are 30° and 120° (all angles from the vertical axis).