Figure 6.
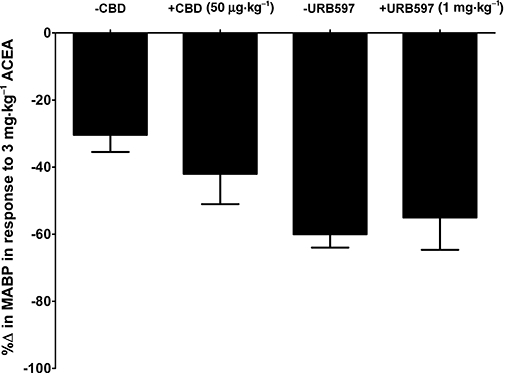
Receptor-mediated effects of (-)-cannabidiol (CBD). The role of CBD as either a CB1 antagonist or potential fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitor was investigated by comparing the effects of CBD (50 µg·kg−1) and the selective FAAH inhibitor, URB597 (1 mg·kg−1), on arachidonyl-2¢-chloroethylamide (ACEA) (3 mg·kg−1)-mediated vascular responses. Agonist-induced changes in mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) were recorded and expressed as a percentage change in MABP (%Δ; n = 4 for each treatment).
