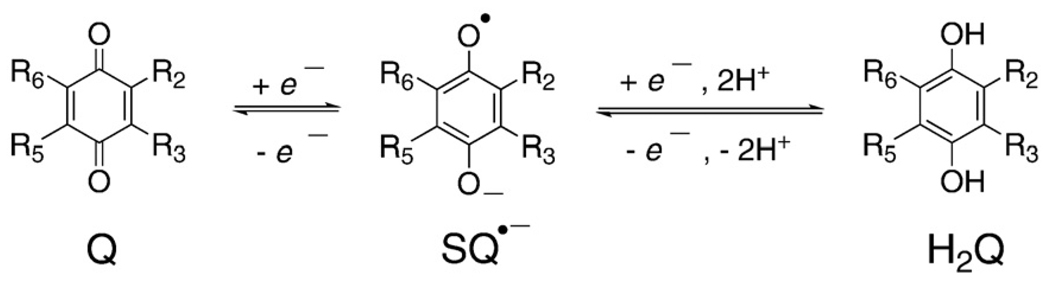
Fig. 1.
Shown are the basic structures of quinones, semiquinones, and corresponding hydroquinones. We show here the dominant species of each component of the triad that would be present in aqueous solution at pH 7. For example, for 1,4-hydroquinone the pKa's are 9.8 and 11.4 for the first and second protons of the phenoxyl moieties, respectively [11,12]. The pKa of the protonated 1,4-semiquinone radical (SQH•) is 4.1 [13,14]; thus, it is shown as the radical anion.