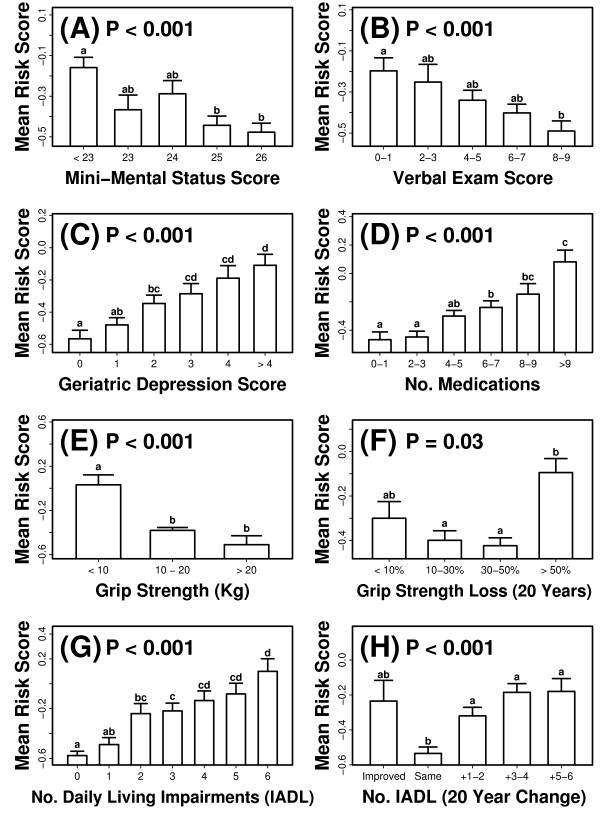
Figure 10.
Risk scores generated from the 13-variable index are associated with multiple outcomes among subjects surviving the follow-up period (mean follow-up time: 20 years). Risk scores were calculated from baseline measures for all 4097 subjects and standardized to have a mean of zero and standard deviation of one. Outcome measures were available for n = 923 to 1296 subjects, and included (A) Mini-mental status exam score (0 - 26 point scale; n = 98 - 257 per group), (B) California Verbal Learning Test (10 minute delay, free recall; 0 - 9 point scale; n = 91 - 275 per group), (C) Geriatric depression score (0 - 15 point scale; n = 79 - 225 per group), (D) total number of prescription medications listed by each subject (n = 111 - 336 per group), (E) average of right and left hand grip strength (kg) (n = 79 - 763 per group), (F) change in average grip strength between the first and ninth visits (n = 79 - 389 per group), (G) reported number of impairments associated with daily living (n = 84 - 359 per group) and (H) the difference in reported number of daily living impairments between the first and ninth visits (n = 41 - 357 per group). The p-value listed in each panel was generated from an F-test of between-group differences in mean risk score (i.e., one way analysis of variance). Lowercase letters above each bar correspond to results from post hoc Tukey-Kramer comparisons, with significant differences between groups that do not share the same letter (P < 0.05).