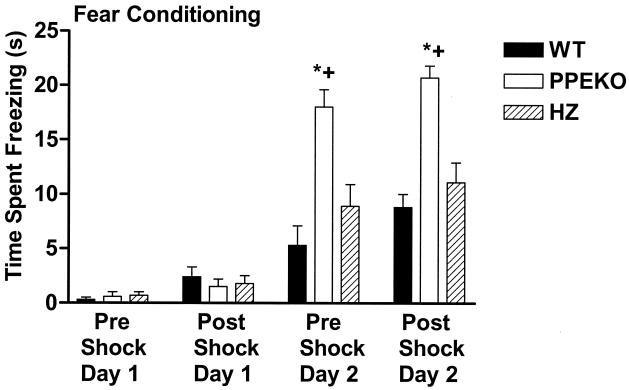
Figure 1.
Alterations in fear conditioning in WT mice, PPEKO mice with both alleles eliminated, and preproenkephalin HZ knockout mice with only one allele eliminated (HZ). The amount of time in a 30-sec period in which the animal exhibited freezing behavior (mean ± SEM) was assessed in animals during an auditory stimulus before (Pre Shock) and after (Post Shock) foot shock on 2 consecutive days (Days 1 and 2). Freezing behavior observed during the first day of auditory stimulation that served as the neutral stimulus (Pre Shock, Day 1) did not differ from the first day of shock, which served as the shock stimulus (Post Shock, Day 1). The PPEKO and HZ groups displayed significantly greater freezing responses during the second day of auditory stimulation, which served as a measure of fear conditioning (Pre Shock, Day 2), and all three groups displayed significantly greater freezing responses during the second day of shock, which served as the fear + shock condition (Post Shock, Day 2) (data not shown). PPEKO mice displayed significantly greater freezing responses during the second day of auditory stimulation both before (Pre Shock, Day 2, fear condition) and after (Post Shock, Day 2, fear + shock condition) shock relative to either WT (*) or HZ (✚) mice. Significant differences were observed among genotypes [ANOVA F(2,28) = 22.32; Tukey's t test, P < 0.0001], across conditions [F(3,18) = 184.08, P < 0.0001], and for the interaction between genotypes and conditions [F(6,84) = 12.54, P < 0.0001]. Variability as a function of squads of testing failed to account for any significant results.