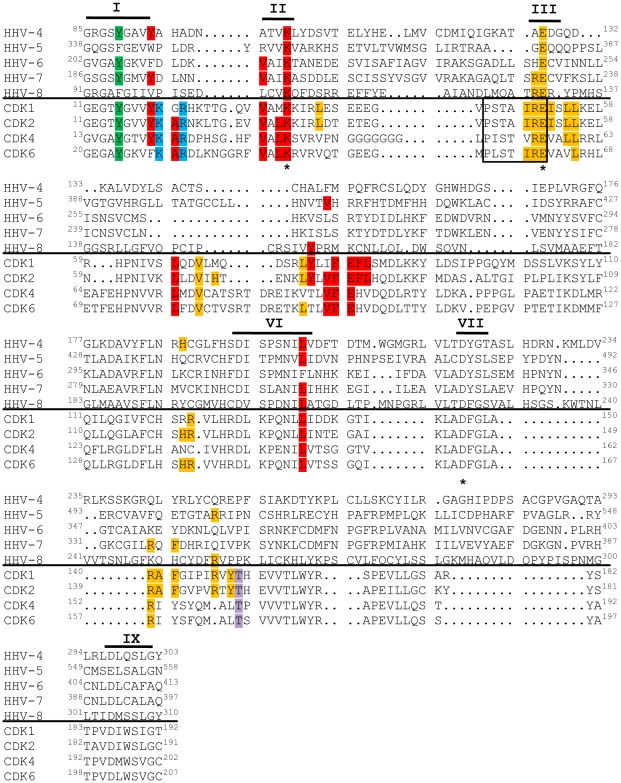
Figure 7. v-Cdks lack conserved cellular Cdk residues that allow for the regulation of kinase activity.
The amino acid sequences of the kinase domains of the indicated viral (top) and human (bottom) Cdks were aligned. Conserved kinase subdomains are indicated with Roman numerals [118]. The residue corresponding to tyrosine 15 of Cdk2 is shown in green. The residue corresponding to threonine 160 of Cdk2 is shown in lavender. Amino acids that mediate cellular Cdk binding to p27 [119], a member of the Cip/Kip class of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, are shown in red. Amino acids that mediate cellular Cdk binding to p16 [120], a member of the INK family of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, are shown in blue. The cyclin-binding PSTAIRE sequence in the cellular Cdks is boxed [121], and other residues shown to be important for CDK2 binding to Cyclin A are shown in orange [121]. The catalytic triad residues are marked with asterisks (*) [118].