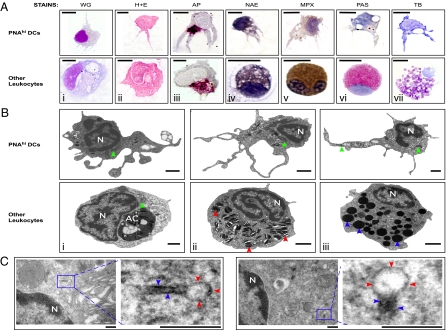
Fig. 3.
Morphological characterization of zebrafish DCs. PNAhi myelomonocytes were isolated from WKM (A and B) or skin (C) by FACS. (A) Cells were stained for WG, H&E, AP (magenta precipitate), NAE (black precipitate), MPX (brown precipitate), PAS (red precipitate), and TB (purple precipitate). (Upper) Putative DCs for each stain. (Lower) Positive staining controls: Mφs (i–iii), monocyte (iv), neutrophil (v), eosinophil (vi), and mast cell (vii). (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (B) TEM was performed to examine the ultrastructure of PNAhi myelomonocytes. (Upper) DCs. (Lower) Other leukocytes: Mφ (i), neutrophil (ii), and eosinophil (iii). Denoted features include nucleus (N), apoptotic corpse (AC), cigar-shaped granules (red arrowheads), round, electron-dense granules (blue arrowheads), and mitochondria (green arrowheads). (Scale bar: 1 μm.) (C) TEM analysis of Birbeck-like granules from PNAhi DCs in skin. Magnified granule regions: vacuole (red arrowheads) and rod structure (blue arrowheads). (Scale bar: 200 nm.)