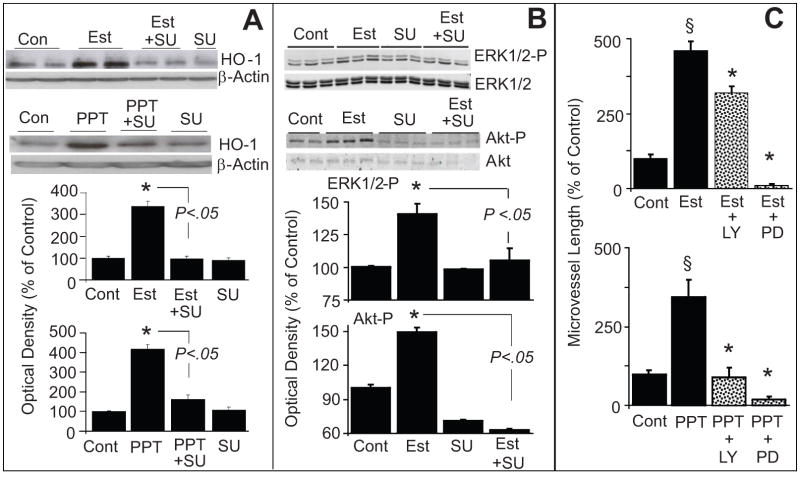
Figure 5.
(A) Bar graph and representative Western blots demonstrating that inhibition of tyrosine kinase with SU5416 (SU) abrogates the stimulatory effects of estradiol and PPT on HO-1 expression in EPCs. EPCs were pretreated with SU (5μmol/L) for 15 minutes and subsequently estradiol (Est; 10nmol/L) or PPT (100nmol/L) was added for an additional 4 hours. HO-1 expression was assayed in the lysates with β-actin as control. Bargraph depicts the densitometry analysis of the HO-1 bands, which were normalize to β-actin. * p<0.05 versus vehicle treated control.
Panel B: Depicts the modulatory effects of SU5416 (SU) on estradiol-induced ERK1/2 and Akt phosphorylation in EPCs. Cells were pretreated with SU for 15 minutes and subsequently estradiol (100nmol/L) was added for an additional 10 minutes. Cell lysates were prepared and expression of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and Akt were analysed by Western blotting. For normalization non-phosphorylated ERK1/2 and Akt were used. Bar graph depicts the densitometry analysis of the phosphorylated ERK1/2 (ERK1/2-P) and Akt (Akt-P) bands, which were normalize to ERK1/2 and Akt, respectively. * p<0.05 versus vehicle treated control. Values represent means±SEM.
(C) Bar graph showing the inhibitory effects of LY294002 (Akt inhibitor; LY; 10μmol/L) and PD98059 (ERK1/2-P inhibitor; PD; 10μmol/L) on estradiol (Est; 10nmol/L) and PPT (100nmol/L) induced capillary formation by EPCs. EPCs were pretreated for 15 minutes with either LY or PD and subsequently Est or PPT added for another 4hoursand capillary formation analyzed microscopically at 4x magnifcation. * p<0.05 vs Estradiol or PPT alone.