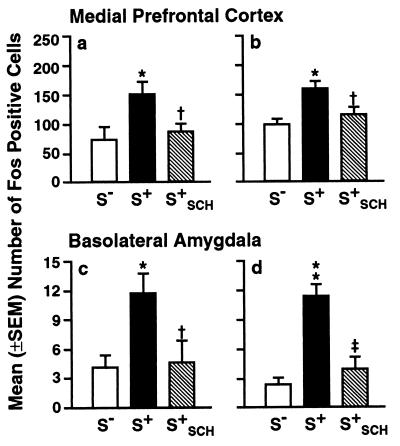
Figure 2.
Fos-immunoreactive nuclei in rats after exposure to the cocaine S+, S−, and S+ preceded by administration of SCH 39166 (S+SCH) in the immediate (a and c) and 4-month delayed (b and d) tests. Compared with the S− control condition, the number of Fos-immunoreactive nuclei was significantly increased after exposure to the cocaine S+ in the basolateral amygdala and medial prefrontal cortex (see also caption of Fig. 3), both in the immediate and delayed testing conditions. SCH 39166 reversed the effects of the cocaine S+ on Fos expression. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (different from the S− condition). †, P < 0.05, ‡, P < 0.01 (different from the S+ condition).