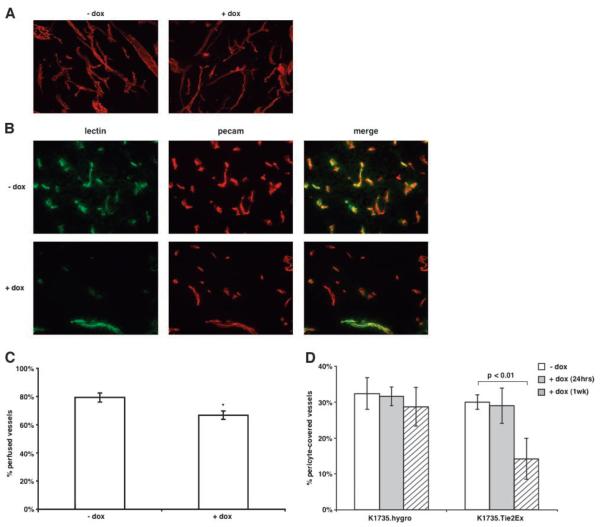
FIGURE 3.
Effect of Tie2Ex on tumor vessel morphology, perfusion, and maturity. A. Thick (60 μm) sections of tumors from mice untreated or treated with doxycycline (18 h) were stained with an anti-CD31 (PECAM) antibody followed by Texas red-conjugated secondary antibody. Tumor sections were viewed using a confocal microscope and the projected images are shown (total magnification, ×100). B. Tumor-bearing mice receiving no doxycycline or doxycycline (18 h) were injected with FITC-conjugated tomato lectin via tail vein to label vessels before euthanasia. Thin (10 μm) sections were stained with an anti-CD31 (PECAM) antibody followed by Texas red-conjugated secondary antibody. Representative images of tumor sections from doxycycline-treated or untreated mice (total magnification, ×200). C. All vessels from the thin tumor sections were counted and the percent of PECAM0positive vessels (total vessels) that are FITC positive (perfused vessels) was calculated. Values were plotted on a histogram plot as the percentage of perfused vessels. *, P < 0.01, t test. D. Frozen tumor sections from K1735.hygro and K1735.Tie2Ex tumors untreated or treated with doxycycline for 24 h and 1 wk were stained with anti-smooth muscle actin antibody and anti-CD31 antibody to identity pericyte-covered vessels. All vessels were counted and plotted as a histogram as percentage of vessels pericyte-covered. Histogram plot represents values obtained from counting vessels in two sections of at least three different tumors for each group. Student’s t test statistical analysis was done. P < 0.01 was considered highly significant.