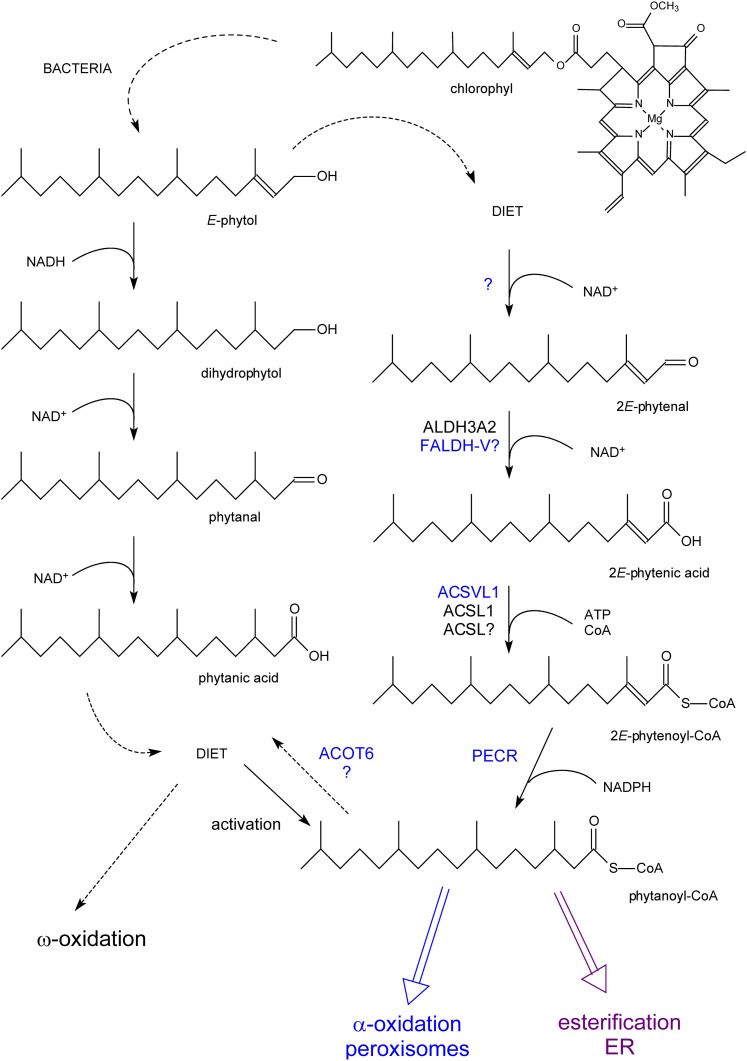
Fig. 2.
Formation of phytanic acid from phytol and its metabolism. Phytol, derived from chlorophyll, can be converted to phytanic acid by rumen bacteria (left side) and taken up via the diet or to phytanoyl-CoA in mammals with phytenoyl-CoA as intermediate (right side). Phytanoyl-CoA can be incorporated in lipids (esterification), shortened by α-oxidized, or hydrolyzed back to phytanic acid. In cases where α-oxidation is impaired, phytanic acid will be degraded starting from the ω-end (ω-oxidation; see supplementary Fig. II). Enzymes printed in blue are associated with peroxisomes. Reactions for which the responsible enzyme have not yet been clarified are marked by a question mark.