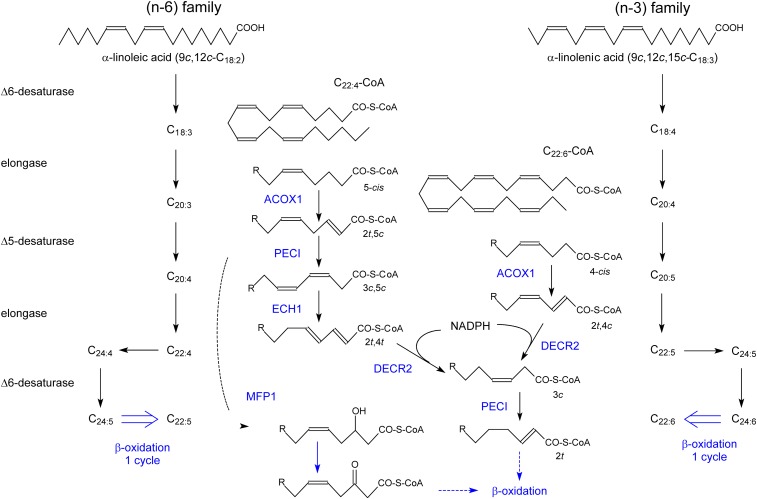
Fig. 7.
Formation and degradation of PUFA. Starting from the essential FAs oleic acid (not shown), linoleic acid (left), and linolenic acid (right), the various (n-9)-, (n-6)- and (n-3)-PUFA are formed in sequential steps (at the level of CoA-ester). The formation of 22:4(n-9) (not shown), 22:5(n-6), and 22:6(n-3) involves an elongation, a Δ6-desaturase, followed by one β-oxidation cycle in the peroxisomes. In the middle, the degradation of FAs with a 5-cis double bond (left) or a 4-cis double bond (right), either MUFAs or PUFAs such as arachidonoyl-CoA or DHA-CoA, is depicted. Enzymes/reactions in blue are associated with peroxisomes.