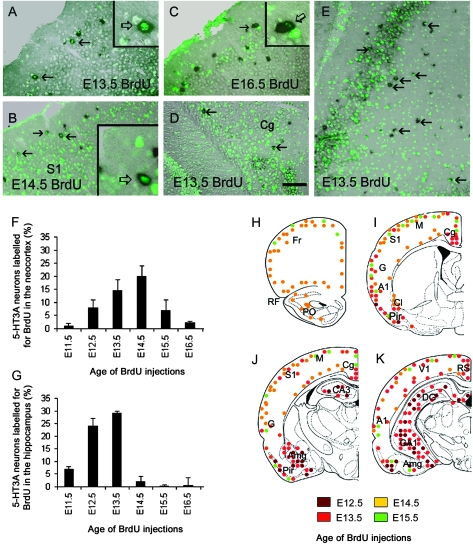
Figure 4.
Birth-dating of telencephalic 5-HT3A interneurons. (A–E) Simultaneous detection of 5-HT3A transcripts (black) and BrdU (green) in coronal sections at the level of the cerebral cortex (A–C), the cingulated cortex (D) and the hippocampus (E) in P25 wild-type mice. Age of pulse injection is indicated on the images. (A–C) Coronal sections taken at the level of the primary somatosensory cortex showing double-labeled cells in the supragranular layers (arrows). (D) Coronal section taken at the level of the cingulate cortex. (F,G) Histograms showing the percentage of 5-HT3A-expressing cells labeled for BrdU after a pulse injection at a given age, quantified in the neocortex (F) and the hippocampus (G). Note that the peak of genesis of cortical 5-HT3A-expressing cells takes place around E14.5. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (percentage of double-labeled cells over the 5-HT3A-postive cells). (H–K) Drawings showing the location and date of genesis of 5-HT3A-expressing cells. Drawings are presented from rostral (H) to caudal (K). A1, auditory cortex; Amg, amygdala; CA1-3, field CA1-3 of the hippocampus; Cl, claustrum; Cg, cingulate cortex area; DG, dentate gyrus; Fr, Frontal cortex area G, gustatory cortex area; M, motor cortex area; Pir, piriform cortex; PO, primary olfactory cortex; RF, Rhinal fissure; RS, retrosplenial cortex; S1, somatosensory cortex area; V1, visual cortex area. Scale bar: (A–D) 200 μm; (E) 250 μm.